




Next: Regularizing smooth data with
Up: Three-dimensional seismic data regularization
Previous: Acknowledgments
Choice of regularization and numerical results
This chapter addresses the problem of choosing appropriate
regularization and preconditioning operators. Such a choice plays a
crucially important role in iterative data regularization. I discuss
three strategies appropriate for different kinds of data:
- 1.
- Smoothly varying surfaces are regularized with recursive helical
smoothers based on the tension-spline theory.
- 2.
- The local plane-wave model is often suitable for characterizing
different kinds of seismic data. Such data are successfully
regularized with plane-wave destructor filters.
- 3.
- Seismic reflection data exhibit additional degrees of
predictability because of multiple coverage. They can be regularized
with finite-difference offset continuation filters. Among the three
methods being discussed, the offset continuation approach is the
most innovative. The theory behind it is explained in
Chapter
![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) .
.
Combining the constructed regularization operator 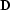 with the
appropriate forward operator
with the
appropriate forward operator 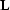 , discussed in
Chapter
, discussed in
Chapter ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) , we obtain a complete problem formulation
in the form of system (
, we obtain a complete problem formulation
in the form of system (![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) ) or (
) or (![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) ). This
chapter is the culmination of this dissertation. It contains final
numerical experiments that test and illustrate the main concepts
developed in other chapters.
). This
chapter is the culmination of this dissertation. It contains final
numerical experiments that test and illustrate the main concepts
developed in other chapters.





Next: Regularizing smooth data with
Up: Three-dimensional seismic data regularization
Previous: Acknowledgments
Stanford Exploration Project
12/28/2000
![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) .
.
![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) .
.
![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) , we obtain a complete problem formulation
in the form of system (
, we obtain a complete problem formulation
in the form of system (![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) ) or (
) or (![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) ). This
chapter is the culmination of this dissertation. It contains final
numerical experiments that test and illustrate the main concepts
developed in other chapters.
). This
chapter is the culmination of this dissertation. It contains final
numerical experiments that test and illustrate the main concepts
developed in other chapters.