




Next: Regularizing reflection seismic data
Up: Plane-wave destruction in 3-D
Previous: Factorizing plane waves
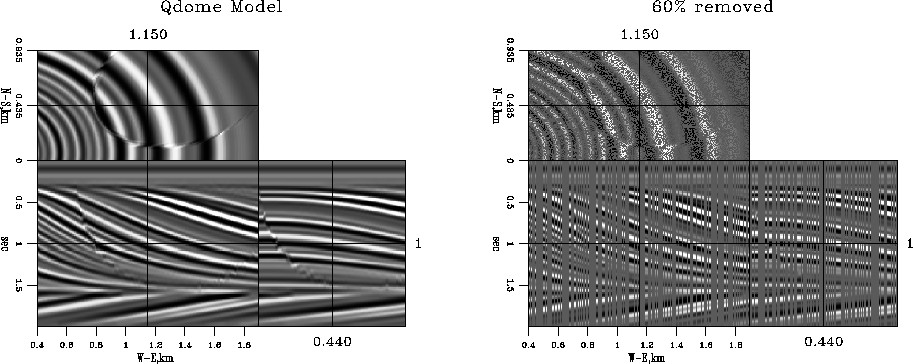
qdome
Figure 27 Claerbout's ``qdome'' synthetic
model. Left: original model. Right: input to interpolation (60% of
the traces removed).




 qslope
qslope
Figure 28 Plane-wave slope estimates in
the x and y directions (left and right plots, respectively) from
the ``qdome'' model. Top: estimated from the original model. Bottom:
estimated from the decimated model.
![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/movie.gif)





Figure ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) shows Claerbout's ``qdome'' synthetic model
Claerbout (1993, 1999), which models a seismic image of a
complicated sedimentary geology. In a data regularization experiment,
I randomly remove 60% of the traces in the original model, arriving
at the missing data model shown in the right plot of
Figure
shows Claerbout's ``qdome'' synthetic model
Claerbout (1993, 1999), which models a seismic image of a
complicated sedimentary geology. In a data regularization experiment,
I randomly remove 60% of the traces in the original model, arriving
at the missing data model shown in the right plot of
Figure ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) . The 3-D slope estimates from the input data
are shown in the bottom plots of Figure
. The 3-D slope estimates from the input data
are shown in the bottom plots of Figure ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) . The
estimates fairly accurately match the slope estimates obtained from
the original model (top plots in Figure
. The
estimates fairly accurately match the slope estimates obtained from
the original model (top plots in Figure ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) ). The
missing-data interpolation result is shown in Figure
). The
missing-data interpolation result is shown in Figure ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) .
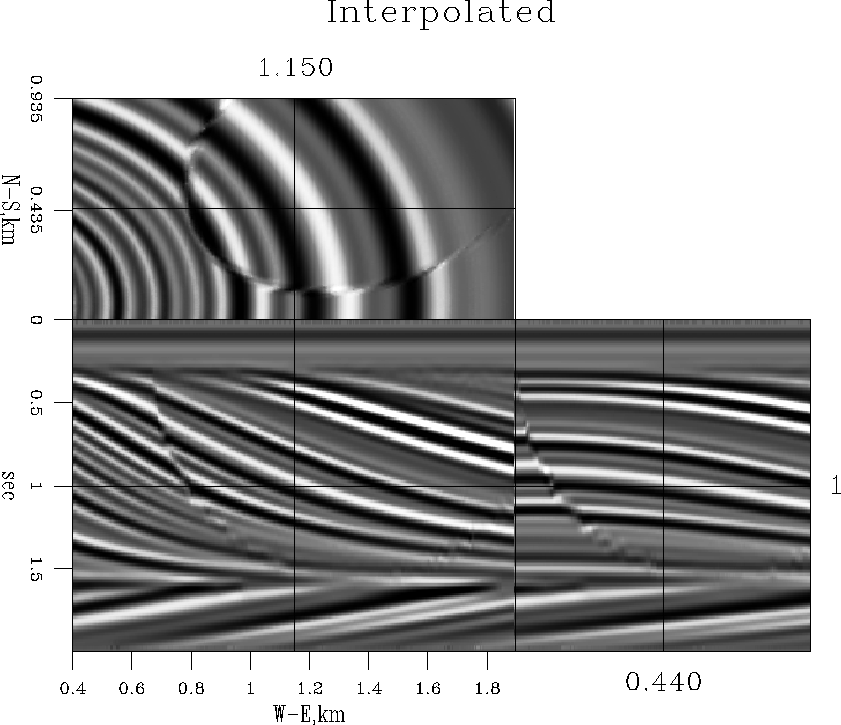
Most of the original signal has been successfully restored. Some of
the fault sharpness is lost in the interpolation result, but all the
curved and planar events are accurately preserved.
Clapp (2000a) reports a successful interpolation
result using a more severe decimation of the same synthetic model.
However, he assumes a prior knowledge of the local dip field instead
of estimating the dips from the decimated data.
.
Most of the original signal has been successfully restored. Some of
the fault sharpness is lost in the interpolation result, but all the
curved and planar events are accurately preserved.
Clapp (2000a) reports a successful interpolation
result using a more severe decimation of the same synthetic model.
However, he assumes a prior knowledge of the local dip field instead
of estimating the dips from the decimated data.
pmiss
Figure 29 Result of missing-data
interpolation with a 3-D local plane-wave destruction filter.
Compare with Figure ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) . .
|
|  |










Next: Regularizing reflection seismic data
Up: Plane-wave destruction in 3-D
Previous: Factorizing plane waves
Stanford Exploration Project
12/28/2000


![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/movie.gif)
![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) shows Claerbout's ``qdome'' synthetic model
Claerbout (1993, 1999), which models a seismic image of a
complicated sedimentary geology. In a data regularization experiment,
I randomly remove 60% of the traces in the original model, arriving
at the missing data model shown in the right plot of
Figure
shows Claerbout's ``qdome'' synthetic model
Claerbout (1993, 1999), which models a seismic image of a
complicated sedimentary geology. In a data regularization experiment,
I randomly remove 60% of the traces in the original model, arriving
at the missing data model shown in the right plot of
Figure ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) . The 3-D slope estimates from the input data
are shown in the bottom plots of Figure
. The 3-D slope estimates from the input data
are shown in the bottom plots of Figure ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) . The
estimates fairly accurately match the slope estimates obtained from
the original model (top plots in Figure
. The
estimates fairly accurately match the slope estimates obtained from
the original model (top plots in Figure ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) ). The
missing-data interpolation result is shown in Figure
). The
missing-data interpolation result is shown in Figure ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) .
Most of the original signal has been successfully restored. Some of
the fault sharpness is lost in the interpolation result, but all the
curved and planar events are accurately preserved.
Clapp (2000a) reports a successful interpolation
result using a more severe decimation of the same synthetic model.
However, he assumes a prior knowledge of the local dip field instead
of estimating the dips from the decimated data.
.
Most of the original signal has been successfully restored. Some of
the fault sharpness is lost in the interpolation result, but all the
curved and planar events are accurately preserved.
Clapp (2000a) reports a successful interpolation
result using a more severe decimation of the same synthetic model.
However, he assumes a prior knowledge of the local dip field instead
of estimating the dips from the decimated data.
![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) .
.
