




Next: Proof of validity
Up: Offset continuation for reflection
Previous: Offset continuation for reflection
Most of the contents of this chapter refer to the following linear
partial differential equation:
| 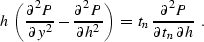 |
(140) |
Equation (![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) ) describes an artificial
(non-physical) process of transforming reflection seismic data
P(y,h,tn) in the offset-midpoint-time domain. In
equation (
) describes an artificial
(non-physical) process of transforming reflection seismic data
P(y,h,tn) in the offset-midpoint-time domain. In
equation (![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) ), h stands for the half-offset
(h=(r-s)/2, where s and r are the source and the receiver
coordinates), y is the midpoint (y=(r+s)/2), and tn is the time
coordinate after normal moveout correction is applied:
), h stands for the half-offset
(h=(r-s)/2, where s and r are the source and the receiver
coordinates), y is the midpoint (y=(r+s)/2), and tn is the time
coordinate after normal moveout correction is applied:
| 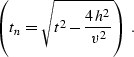 |
(141) |
The velocity v is assumed to be known a priori.
Equation (![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) ) belongs to the class of linear
hyperbolic equations, with the offset h acting as a time-like
variable. It describes a wave-like propagation in the offset
direction.
) belongs to the class of linear
hyperbolic equations, with the offset h acting as a time-like
variable. It describes a wave-like propagation in the offset
direction.





Next: Proof of validity
Up: Offset continuation for reflection
Previous: Offset continuation for reflection
Stanford Exploration Project
12/28/2000
![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) ) describes an artificial
(non-physical) process of transforming reflection seismic data
P(y,h,tn) in the offset-midpoint-time domain. In
equation (
) describes an artificial
(non-physical) process of transforming reflection seismic data
P(y,h,tn) in the offset-midpoint-time domain. In
equation (![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) ), h stands for the half-offset
(h=(r-s)/2, where s and r are the source and the receiver
coordinates), y is the midpoint (y=(r+s)/2), and tn is the time
coordinate after normal moveout correction is applied:
), h stands for the half-offset
(h=(r-s)/2, where s and r are the source and the receiver
coordinates), y is the midpoint (y=(r+s)/2), and tn is the time
coordinate after normal moveout correction is applied:
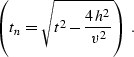
![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) ) belongs to the class of linear
hyperbolic equations, with the offset h acting as a time-like
variable. It describes a wave-like propagation in the offset
direction.
) belongs to the class of linear
hyperbolic equations, with the offset h acting as a time-like
variable. It describes a wave-like propagation in the offset
direction.