I now demonstrate the analogous derivation for the ![]() specular
reflection coefficient. Again, the least-squares solution is given by
(10):
specular
reflection coefficient. Again, the least-squares solution is given by
(10):
| |
(38) |
For a ![]() reflection, the incident P-wave scalar is the same
as (27):
reflection, the incident P-wave scalar is the same
as (27):
| |
(39) |
However, the reflected S1-wave scalar needs to be evaluated given (4), (24) and (25):
| |
(40) |
In deriving (40) I have taken the farfield WKBJ approximation of the displacement vector wavefield gradient and divergence terms given in (30)-(31).
Substituting (39) and (40) into (38) and performing the required t integrations, one obtains
| |
(41) |
| |
||
| (42) |
Now ![]() is now evaluated at the total incident P plus
reflected S ray traveltime
is now evaluated at the total incident P plus
reflected S ray traveltime ![]() . The subscripts on
. The subscripts on
![]() and
and ![]() indicate that the Lamé parameters should be
evaluated at the receiver positions
indicate that the Lamé parameters should be
evaluated at the receiver positions ![]() , and the
, and the ![]() symbol still
signifies a convolution of the surface data
symbol still
signifies a convolution of the surface data ![]() with the estimated
P-wave source wavelet w1. The P-wave autocorrelation integral is
the same as the
with the estimated
P-wave source wavelet w1. The P-wave autocorrelation integral is
the same as the ![]() case:
case:
| |
(43) |
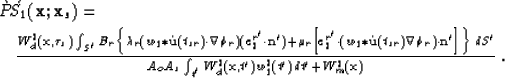 |
||
| (44) |
Equation (44) gives the least-squares
elastic wavefield integral solution for ![]() specular reflectivity.
It also can be slightly simplified further by noting that
specular reflectivity.
It also can be slightly simplified further by noting that
| |
(45) |
which follows from the S-wave eikonal equation in (15),
where ![]() is the
S-wave velocity evaluated at each receiver position
is the
S-wave velocity evaluated at each receiver position ![]() .
.