Next: Example 3: Leveled inverse
Up: EXAMPLES
Previous: Example 1: Inverse interpolation
The next test example is the velocity transform inversion with a CMP
gather from the Mobil AVO dataset
Lumley et al. (1994); Lumley (1994); Nichols (1994). I use Jon
Claerbout's veltran program Claerbout (1995b) for
anti-aliased velocity transform with rho-filter preconditioning
and compare three different pairs of operators for inversion. The
first pair is the CMP stacking operator with the ``migration''
weighting function 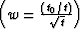 and its adjoint. The second pair is
the ``pseudo-unitary'' velocity transform with the weighting
proportional to
and its adjoint. The second pair is
the ``pseudo-unitary'' velocity transform with the weighting
proportional to 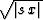 , where x is the offset and s is
the slowness. These two pairs were used in the velocity transform
inversion with the iterative conjugate-gradient solver. The third pair
uses the weight proportional to |x| for CMP stacking and |s| for
the reverse operator. Since these two operators are not exact
adjoints, it is appropriate to apply the method of conjugate
directions for inversion. The convergence of the three different
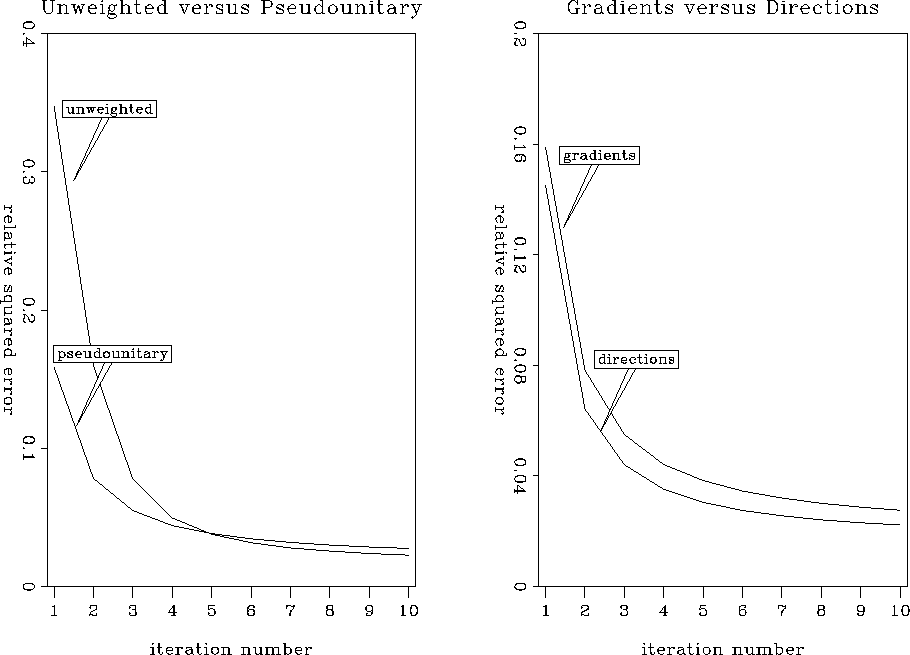
inversions is compared in Figure 4. We can see that the
third method reduces the least-square residual error, though it has a
smaller effect than that of the pseudo-unitary weighting in comparison
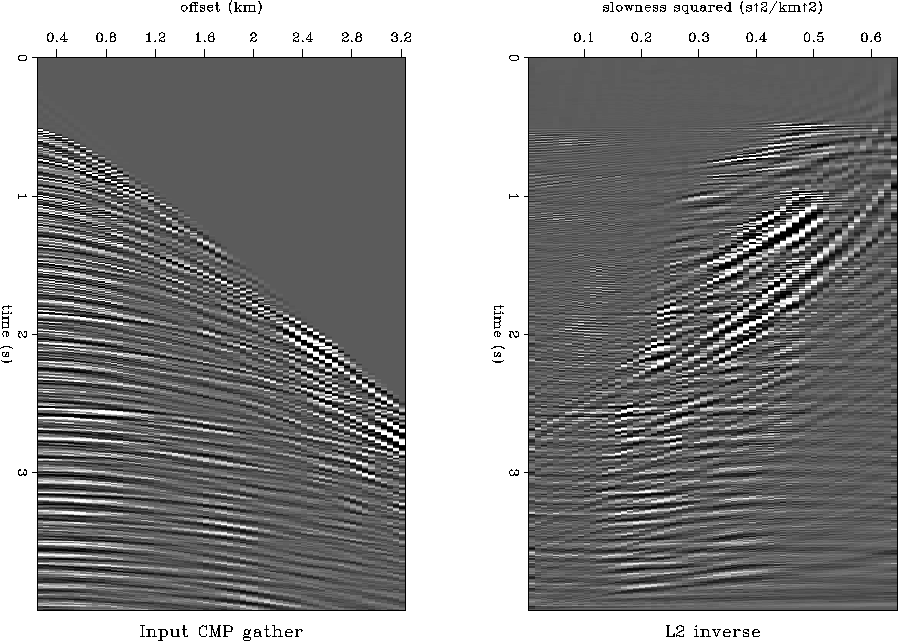
with the uniform one. The results of inversion after 10
conjugate-gradient iterations are plotted in Figures 5 and
6, which are to be compared with the analogous results of
David Lumley 1994 and Dave Nichols
1994.
diritr
, where x is the offset and s is
the slowness. These two pairs were used in the velocity transform
inversion with the iterative conjugate-gradient solver. The third pair
uses the weight proportional to |x| for CMP stacking and |s| for
the reverse operator. Since these two operators are not exact
adjoints, it is appropriate to apply the method of conjugate
directions for inversion. The convergence of the three different
inversions is compared in Figure 4. We can see that the
third method reduces the least-square residual error, though it has a
smaller effect than that of the pseudo-unitary weighting in comparison
with the uniform one. The results of inversion after 10
conjugate-gradient iterations are plotted in Figures 5 and
6, which are to be compared with the analogous results of
David Lumley 1994 and Dave Nichols
1994.
diritr
Figure 4 Comparison of
convergence of the iterative velocity transform inversion. The left
plot compares conjugate-gradient inversion with unweighted (uniformly
weighted) and pseudo-unitary operators. The right plot compares
pseudo-unitary conjugate-gradient and weighted conjugate-direction
inversion.




 dircvv
dircvv
Figure 5 Input
CMP gather (left) and its velocity transform counterpart (right) after
10 iterations of conjugate-direction inversion.




 dirrst
dirrst
Figure 6 The modeled CMP
gather (left) and the residual data (right) plotted at the same scale.










Next: Example 3: Leveled inverse
Up: EXAMPLES
Previous: Example 1: Inverse interpolation
Stanford Exploration Project
9/11/2000