|
|
|
|
Blocky velocity inversion by hybrid norm |
|
|---|
|
l2-lab27
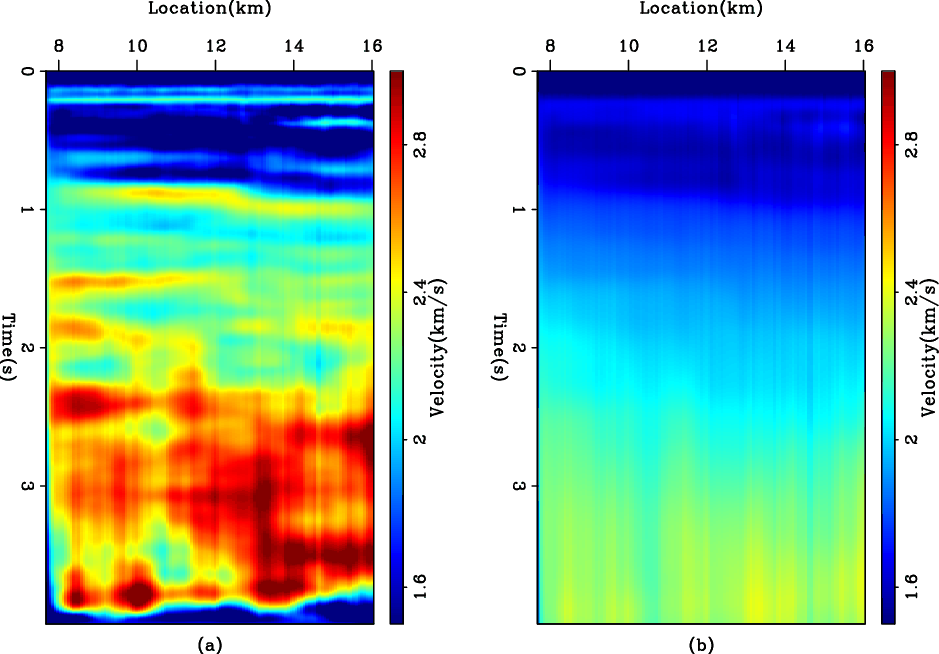
Figure 5. The WG dataset. (a) The interval velocity estimated by using the helix derivative operator as a regularization in the |
|
|
|
|---|
|
hbe-lab29
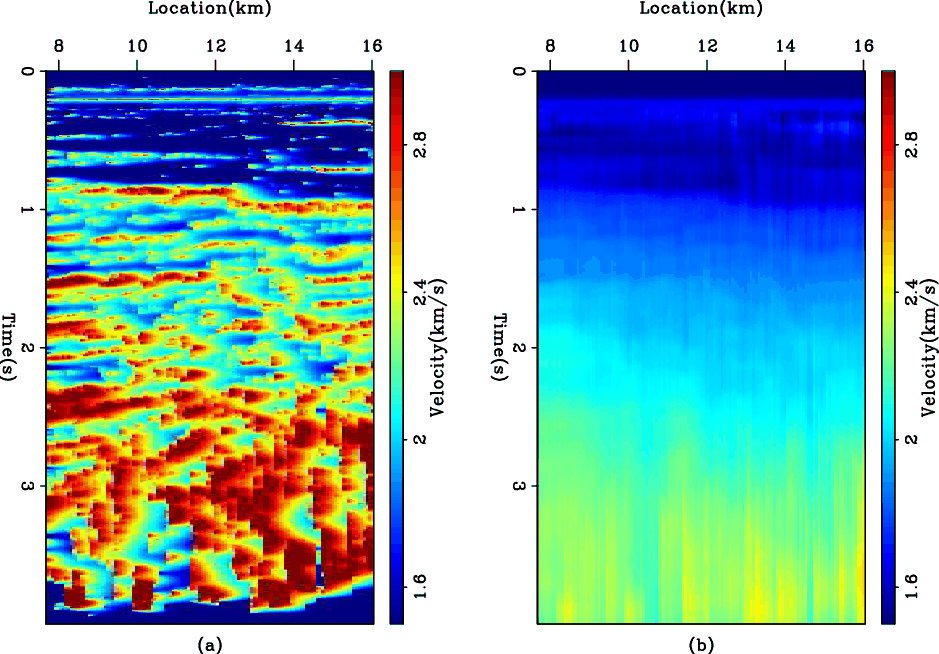
Figure 6. The WG dataset. (a) The interval velocity estimated by using the helix derivative operator as a regularization in the hybrid norm. (b) The reconstructed RMS velocity. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Blocky velocity inversion by hybrid norm |