|
|
|
|
Blocky velocity inversion by hybrid norm |
|
|---|
|
lab0
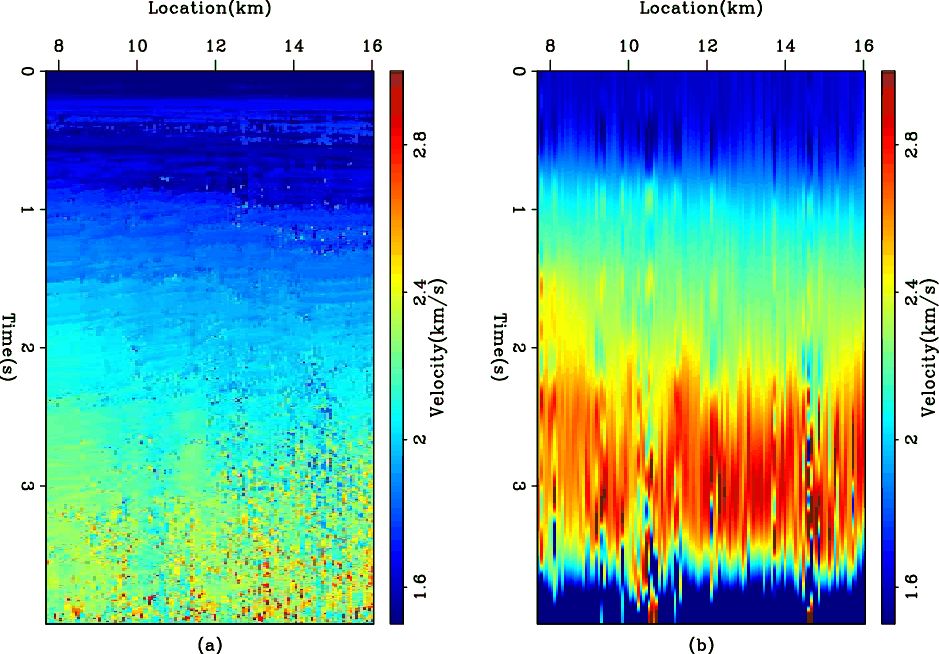
Figure 1. The WG dataset. (a) The input RMS velocity, which is automatically picked from the CMP gathers. (b) The interval velocity by direct dix conversion. |
|
|
|
lab-weight2d
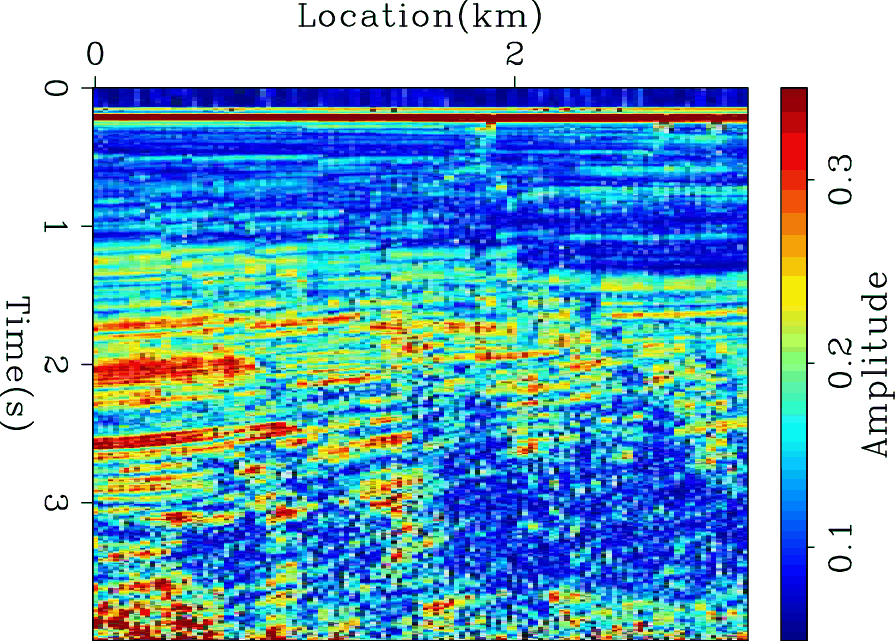
Figure 2. The strength of the picks in the velocity scan of the WG dataset, which is used as the weight before dividing by time. |
|
|---|---|
|
|
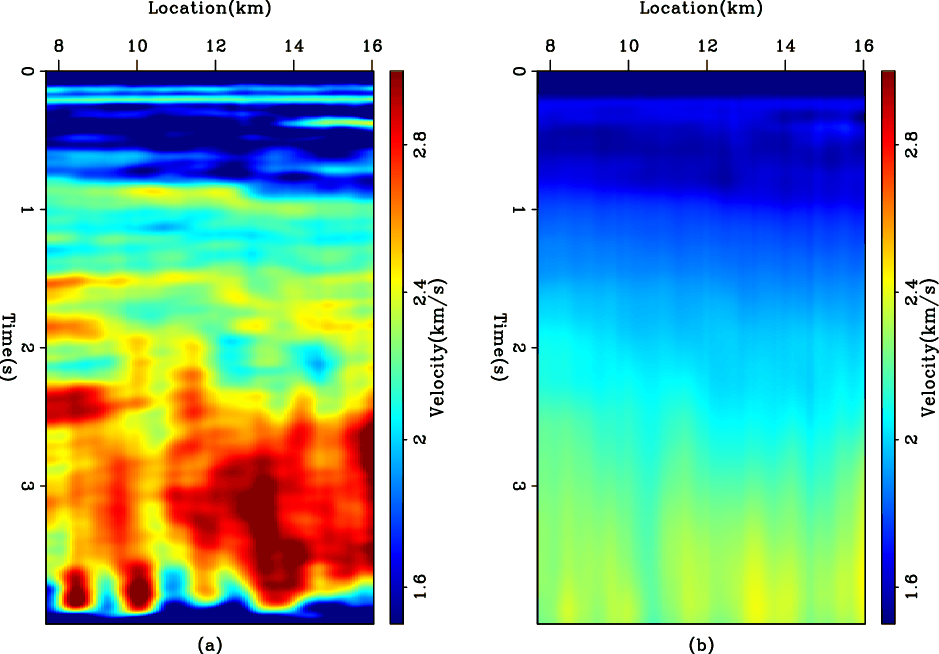
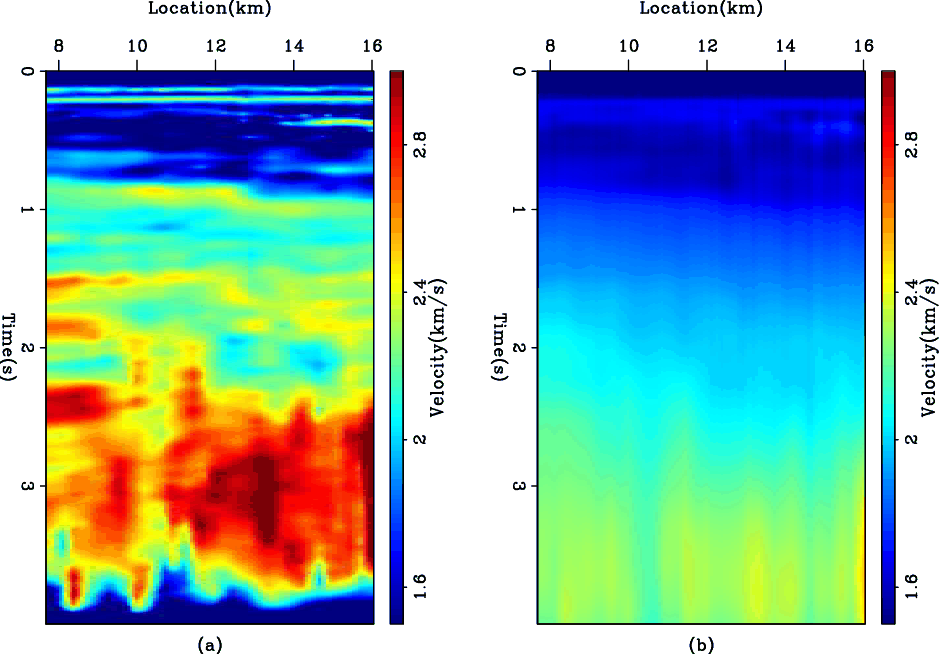
We start by choosing the symmetric Laplacian operator. Figure 3 shows the results of using the ![]() norm and Figure 4 shows the results of using the hybrid norm. Although the two Figures look similar, the hybrid norm shows less smoothing and more detail than the
norm and Figure 4 shows the results of using the hybrid norm. Although the two Figures look similar, the hybrid norm shows less smoothing and more detail than the ![]() norm. The hybrid norm results are still not blocky, because a linear trend in velocity will also result in a zero second derivative. In the next section we attempt to more closely approach the first derivative by using the helix derivative.
norm. The hybrid norm results are still not blocky, because a linear trend in velocity will also result in a zero second derivative. In the next section we attempt to more closely approach the first derivative by using the helix derivative.
|
|---|
|
l2-lab18
Figure 3. The WG dataset. (a) The interval velocity estimated by using the Laplacian operator as a regularization in the |
|
|
|
|---|
|
hbe-lab19
Figure 4. The WG dataset. (a) The interval velocity estimated by using the Laplacian operator as a regularization in the hybrid norm. (b) The reconstructed RMS velocity. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Blocky velocity inversion by hybrid norm |