




Next: Inversion of the pressure
Up: INVERSION OF SYNTHETICS: WATER
Previous: INVERSION OF SYNTHETICS: WATER
The near sea-bottom properties can be estimated using inversion. Since the problem is highly
non-linear, we applied an iterative damped least-squares approach
Levenberg (1944); Lines and Treitel (1984); Marquardt (1963) which
minimizes the misfit between the amplitude spectrum of the theoretical
reflection (equation 2)
or AVO coefficient (equation 4)
and the calculated one (equation 1 and 3).
The misfit function is defined as:
| 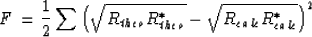 |
(5) |
The star (*) denotes the complex conjugate. R is
either the reflection coefficient or the AVO coefficient, depending on the
data being used. Because of the nonlinearity of the problem, it is important
to make a reasonable initial guess of the parameters.
Once the near seafloor parameters have
been estimated, they can be used to calculate a predicted reflection or AVO
coefficient for all angles of incidence.





Next: Inversion of the pressure
Up: INVERSION OF SYNTHETICS: WATER
Previous: INVERSION OF SYNTHETICS: WATER
Stanford Exploration Project
11/11/1997