Next: Synthetic-data examples of RMO
Up: Anisotropic residual moveout for
Previous: RMO function with arbitrary
The RMO functions derived above can be directly used in a
layered-based vertical updating of the velocity function
after migration.
However, in complex media it is often desirable to invert the depth errors
measured from ADCIGs into velocity-parameter perturbations
through a tomographic procedure.
To be able to apply a tomographic method,
we must perform an additional step to convert
the depth errors measured from ADCIGs into
traveltime errors.
This depth-to-time conversion can be easily
accomplished by slightly rewriting the chain of
partial derivatives in equation 14,
and obtain the following relationship:
| 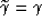 |
(27) |
which can be directly applied to
convert depth errors into traveltime perturbations
to be used in tomography.
It is immediate to verify that in the isotropic case,
in which  ,equation 27 simplifies into the following
relationship:
,equation 27 simplifies into the following
relationship:
| 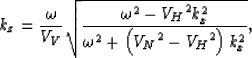 |
(28) |
which is equivalent to the relationship
derived
for isotropic MVA
by Biondi and Symes (2003).





Next: Synthetic-data examples of RMO
Up: Anisotropic residual moveout for
Previous: RMO function with arbitrary
Stanford Exploration Project
11/1/2005
 ,equation 27 simplifies into the following
relationship:
,equation 27 simplifies into the following
relationship: