In order to test the accuracy of our operator we
created a synthetic data set assuming
a constant velocity model of
vp=3000 m/s and vs=1500 m/s,
and four reflectors
having dips of ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,respectively.
,respectively.
We first migrated the data with the wrong velocity, using shot-profile migration for converted waves Rosales and Rickett (2001), and extract angle-domain common-image gathers for converted waves Rickett and Sava (2001). We then applied Stolt residual prestack migration, using the methods described in the previous section.
We show the results of performing migration
followed by residual
prestack migration,
when the initial migration was performed with
the correct P-velocity,
and with the S-velocity ![]() too high.
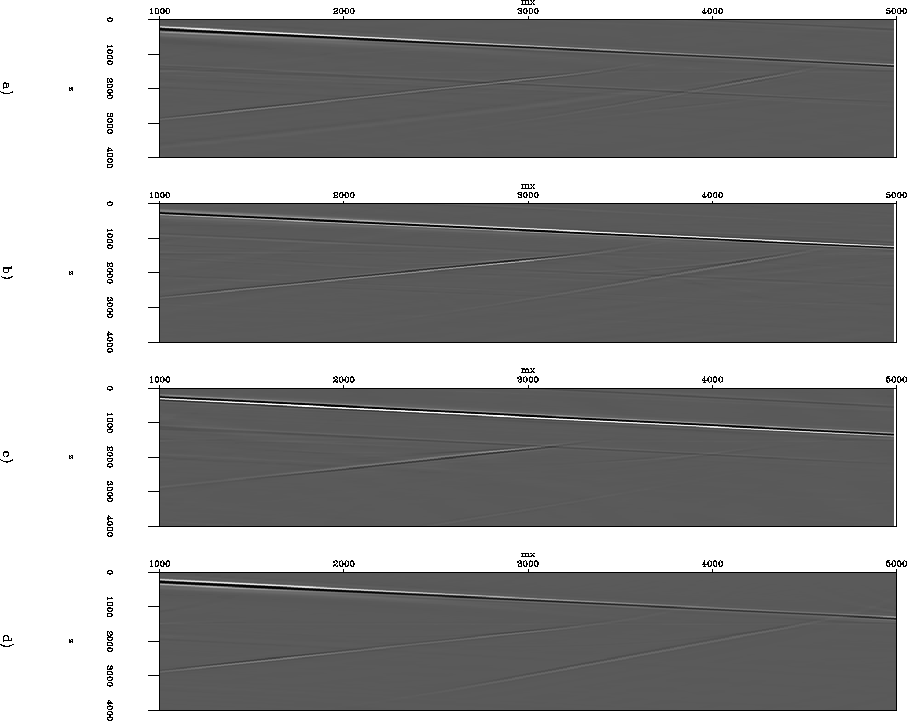
Figure 3 shows a comparison for the zero offset section,
equivalent to
the stack final migrated section, of the residual migration result for
equations (3), (5) and (6) and the
migration with the correct velocity model.
It is possible to
observe that the result with the correct
expression [equation(3)]
produces
an image similar to the image produced by the migration
with the correct velocity.
On the contrary,
when we use the other two expressions we obtain poorly
focused results.
too high.
Figure 3 shows a comparison for the zero offset section,
equivalent to
the stack final migrated section, of the residual migration result for
equations (3), (5) and (6) and the
migration with the correct velocity model.
It is possible to
observe that the result with the correct
expression [equation(3)]
produces
an image similar to the image produced by the migration
with the correct velocity.
On the contrary,
when we use the other two expressions we obtain poorly
focused results.
 |
![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/movie.gif)
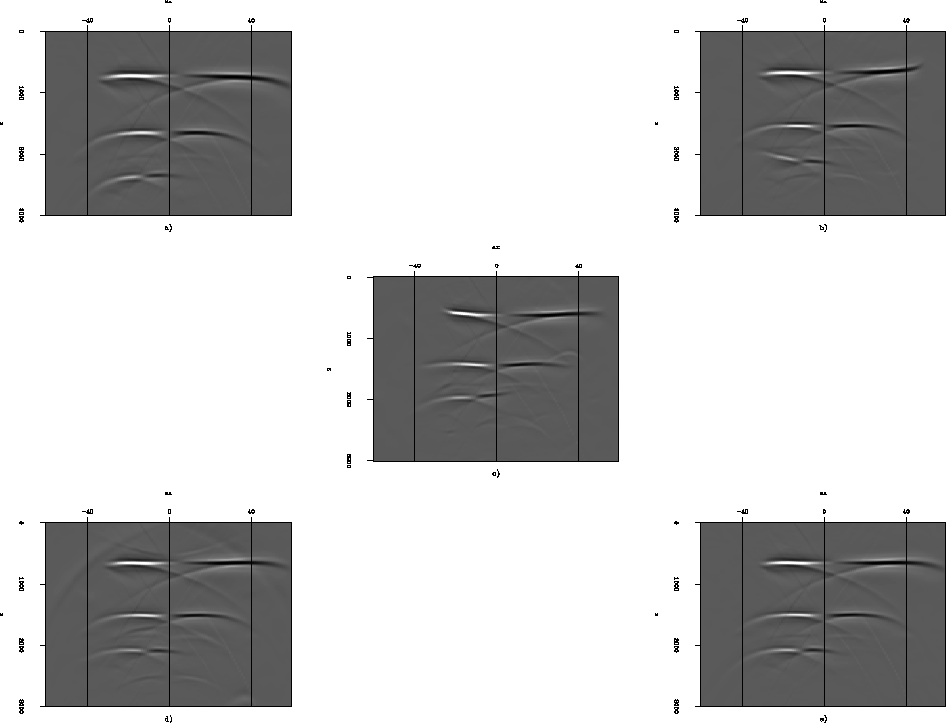
Notice that because of the change in polarity between the negative and positive reflection angles, these zero-offset sections show degraded images. Rosales and Rickett (2001) discuss how to correct for the change in polarity. Therefore, we analyze the common image gathers. Figure 4 shows five common image gather all taken at the same surface location. From left to right: the good migration result, correction with the correct expression [equation (3)], correction with equation (5), correction with equation (6) and the bad migration result. It is possible to observe that the events after residual migration with the correct expression [equation (3)] are flat. Corrections with equations (5) and (6) yield to over and under corrected gathers, respectively.
 |
![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/movie.gif)