 |
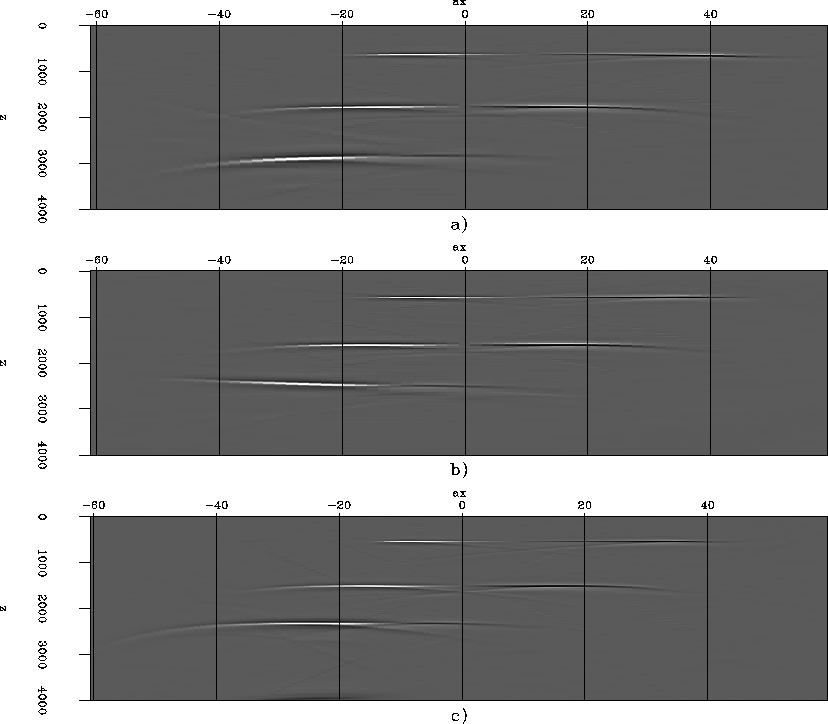
Figure 5 Zero offset section comparison, final migration stack, for: a) migration with
![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/movie.gif)
Since Stolt residual prestack migration is based on the assumption of constant velocity, we will evaluate the accuracy for velocity models having depth dependence.
We create our second synthetic model using the same reflector geometry as the previous section and using a realistic depth velocity model of v0p=1700 m/s with a gradient of 0.15 s-1 and v0s=300 m/s with a gradient of 0.35 s-1,
 |
![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/movie.gif)
As before,
we perform the initial shot profile migration with
a ![]() positive perturbation
in the S-velocity model.
We perform residual migration with the RMS
positive perturbation
in the S-velocity model.
We perform residual migration with the RMS ![]() value at approximately 1.5 km,
and
value at approximately 1.5 km,
and ![]() and
and ![]() .Residual prestack migration could not recover the image correctly
at all depths.
However, we got a good approximation of it.
Figures 5
and 6 show our results.
.Residual prestack migration could not recover the image correctly
at all depths.
However, we got a good approximation of it.
Figures 5
and 6 show our results.
 |
![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/movie.gif)