




Next: Jacobian for Common-azimuth migration
Up: Transformation Jacobians
Previous: Angle-gathers
For the case of offset ray-parameter gathers, we can rewrite the
DSR equation (22) as
| 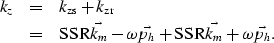 |
|
| (26) |
In this case, the imaging Jacobian becomes
| ![\begin{eqnarray}
\bold W_{p_h}
&=& \left.\frac{d\omega}{dk_z}\right\vert _{{\bf ...
...vec{p_h}\right )\cdot {\bf {p_{h}}}}{4{k_{\rm zr}}}
\right ]^{-1},\end{eqnarray}](img53.gif) |
|
| (27) |
which can be re-arranged as:
| ![\begin{eqnarray}
\bold W_{p_h}
&=&
\left [\left (s-\frac{{\bf {p_{h}}}\cdot{\bf...
...\rm zs}}} -
\frac{\omega s}{{k_{\rm zr}}} \right )
\right ]^{-1}.\end{eqnarray}](img54.gif) |
(28) |
For an arbitrary 2-D reflection geometry (Figure 1),
we can write Equation (28) as
| ![\begin{displaymath}
\bold W_{p_h} =
\left [\left (s-\frac{{\bf {p_{h}}}\cdot{\b...
...ac{1}{\cos \left [\gamma+\alpha\right ]}\right )
\right ]^{-1}.\end{displaymath}](img55.gif) |
(29) |
For flat reflectors, defined by 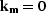 and
and 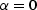 ,
the Jacobian takes the simple form
,
the Jacobian takes the simple form
| 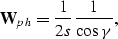 |
(30) |
which is equivalent to the weighting factor introduced by
Wapenaar et al. (1999).
For the case of flat reflectors, we also have
| 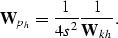 |
(31) |
which explains the opposite behavior of the uncorrected migration
amplitudes for reflection-angle gathers (Figure 10)
and offset ray-parameter gathers (Figure 11).
After we apply the Jacobian weights, we obtain the corrected
angle-gathers shown in Figures 12 and 13.
As expected, the amplitudes are constant for the entire usable
angular range.





Next: Jacobian for Common-azimuth migration
Up: Transformation Jacobians
Previous: Angle-gathers
Stanford Exploration Project
4/30/2001
![\begin{eqnarray}
\bold W_{p_h}
&=& \left.\frac{d\omega}{dk_z}\right\vert _{{\bf ...
...vec{p_h}\right )\cdot {\bf {p_{h}}}}{4{k_{\rm zr}}}
\right ]^{-1},\end{eqnarray}](img53.gif)
![\begin{displaymath}
\bold W_{p_h} =
\left [\left (s-\frac{{\bf {p_{h}}}\cdot{\b...
...ac{1}{\cos \left [\gamma+\alpha\right ]}\right )
\right ]^{-1}.\end{displaymath}](img55.gif)