




Next: Coherent noise attenuation results
Up: Theory review
Previous: Subtraction method
In this section, we describe a method that computes the signal PEF needed
in equations (2) and (4).
Spitz (1999) showed that for uncorrelated
signal and noise, the signal PEF can be expressed in terms of 2 PEF's:
a PEF 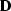 , estimated from the data
, estimated from the data 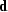 , and a PEF
, and a PEF
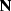 , estimated from the noise model such that
, estimated from the noise model such that
| 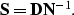 |
(9) |
Equation (9) states that the signal PEF equals the
data PEF deconvolved by the noise PEF. Spitz formulated the problem
in the f-x domain, but the helix transform Claerbout (1998)
permits stable inverse filtering with multidimensional t-x domain filters.





Next: Coherent noise attenuation results
Up: Theory review
Previous: Subtraction method
Stanford Exploration Project
4/29/2001