




Next: 3-D Residual Stolt Migration
Up: Sava: Residual migration
Previous: Stolt Migration
In general, residual migration represents a method of improving the
quality of the image without
having to remigrate the original data,
but rather only applying a transformation to the current
migration image.
stolt
Figure 1 A sketch of Stolt residual migration
|
| 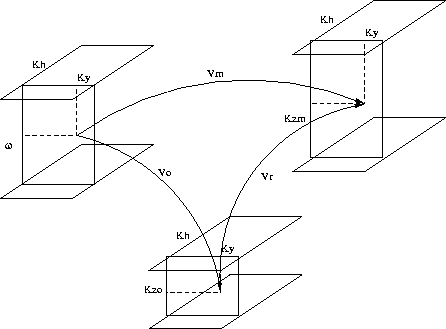 |

In residual prestack Stolt migration (RPrSM), we attempt to correct
the effects of migrating with an inaccurate reference velocity by
applying a transformation to the data that have been transformed to the
Fourier domain (Figure 1). Supposing that the initial
migration was done with the velocity v0, and that the correct
velocity is vm, we can then write
The goal of RPrSM is to obtain kzm from kz0. If we use
the first equation of (4) to substitute  in the second equation of (4), we obtain
in the second equation of (4), we obtain
| ![\begin{displaymath}
\begin{array}
{r}
k_{z_m}=\frac{1}{2}
\sqrt{ \frac{v_0^2}{v_...
...k_{z_0}^2+(k_g+k_s)^2\right]}
{16 k_{z_0}^2}-k_s^2}\end{array}\end{displaymath}](img9.gif) |
(4) |
or
| ![\begin{displaymath}
\begin{array}
{r}
k_{z_m}=
\frac{1}{2}
\sqrt{ \frac{v_0^2}{v...
...[k_{z_0}^2+k_y^2\right]}
{k_{z_0}^2}-(k_y-k_h)^2} .\end{array}\end{displaymath}](img10.gif) |
(5) |
Equation (6) represents the RPrSM
equation in two dimensions. For post-stack data, the same equation
takes the familiar form
| ![\begin{displaymath}
k_{z_m}= \sqrt{ \frac{v_0^2}{v_m^2}\left[k_{z_0}^2+k_y^2\right]-k_y^2}.\end{displaymath}](img11.gif) |
(6) |





Next: 3-D Residual Stolt Migration
Up: Sava: Residual migration
Previous: Stolt Migration
Stanford Exploration Project
6/30/1999


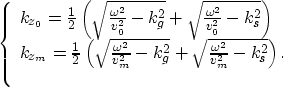
![]() in the second equation of (4), we obtain
in the second equation of (4), we obtain