




Next: Examples
Up: Sava: Residual migration
Previous: 2-D Residual Stolt Migration
The RPrSM equations in three dimensions can be written similarly to
those in two dimensions if we consider the relationship between
source-geophone and midpoint-offset coordinates as follows:
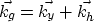
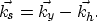
The equivalent prestack residual migration equation in source-geophone
coordinates thus becomes
| ![\begin{displaymath}
\begin{array}
{r}
k_{z_m}=\frac{1}{2}
\sqrt{ \frac{v_0^2}{v_...
...t)^2\right]}
{16k_{z_0}^2}-\vert\vec{k_s}\vert^2} .\end{array}\end{displaymath}](img14.gif) |
(7) |
In midpoint-offset coordinates, the same equation becomes
| ![\begin{displaymath}
\begin{array}
{r}
k_{z_m}=\frac{1}{2}
\sqrt{ \frac{v_0^2}{v_...
...]}
{16k_{z_0}^2}-\vert\vec{k_y}-\vec{k_h}\vert^2} ,\end{array}\end{displaymath}](img15.gif) |
(8) |
which, for the post-stack case, takes the form
| ![\begin{displaymath}
k_{z_m}= \sqrt{ \frac{v_0^2}{v_m^2}\left[k_{z_0}^2+ \vert\vec{k_y}\vert^2\right]-\vert\vec{k_y}\vert^2}.\end{displaymath}](img16.gif) |
(9) |





Next: Examples
Up: Sava: Residual migration
Previous: 2-D Residual Stolt Migration
Stanford Exploration Project
6/30/1999
![]()
![]()
![\begin{displaymath}
\begin{array}
{r}
k_{z_m}=\frac{1}{2}
\sqrt{ \frac{v_0^2}{v_...
...t)^2\right]}
{16k_{z_0}^2}-\vert\vec{k_s}\vert^2} .\end{array}\end{displaymath}](img14.gif)
![\begin{displaymath}
\begin{array}
{r}
k_{z_m}=\frac{1}{2}
\sqrt{ \frac{v_0^2}{v_...
...]}
{16k_{z_0}^2}-\vert\vec{k_y}-\vec{k_h}\vert^2} ,\end{array}\end{displaymath}](img15.gif)