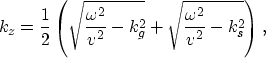Next: 2-D Residual Stolt Migration
Up: Sava: Residual migration
Previous: Introduction
Prestack Stolt migration (PrSM) was summarized as
Claerbout (1985)
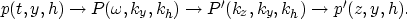
An important component of PrSM is the remapping from the  domain to the (kz,ky,kh) domain, where
domain to the (kz,ky,kh) domain, where  , kz represent,
respectively, the frequency and the vertical wavenumber, and ky,kh
represent the midpoint and offset wavenumbers.
, kz represent,
respectively, the frequency and the vertical wavenumber, and ky,kh
represent the midpoint and offset wavenumbers.
If we consider the alternative representation of the input data in
shot-geophone coordinates, the mapping takes the form
| 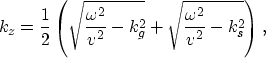 |
(1) |
where
kg and ks stand for, respectively, the geophone and the source
wavenumbers. It is desirable to implement the remapping as a pull
operator, to avoid numerical problems in the inverse Fourier
transform. A detailed discussion on the advantages and disadvantages
of the different mappings is done by Levin
1994.
We can, therefore, express
 as a function of kz from Equation (1) as:
as a function of kz from Equation (1) as:
| ![\begin{displaymath}
\omega^2 = \frac{v^2}{16 k_z^2}
\left[ 4 k_z^2+(k_g-k_s)^2\right]
\left[ 4 k_z^2+(k_g+k_s)^2\right]\end{displaymath}](img6.gif) |
(2) |
or
| ![\begin{displaymath}
\omega^2 = \frac{v^2}{k_z^2}
\left[ k_z^2+k_h^2\right]
\left[ k_z^2+k_y^2\right].\end{displaymath}](img7.gif) |
(3) |





Next: 2-D Residual Stolt Migration
Up: Sava: Residual migration
Previous: Introduction
Stanford Exploration Project
6/30/1999
![]()
![]() domain to the (kz,ky,kh) domain, where
domain to the (kz,ky,kh) domain, where ![]() , kz represent,
respectively, the frequency and the vertical wavenumber, and ky,kh
represent the midpoint and offset wavenumbers.
, kz represent,
respectively, the frequency and the vertical wavenumber, and ky,kh
represent the midpoint and offset wavenumbers.