




Next: Noise removal on Shearer's
Up: SIGNAL-NOISE DECOMPOSITION BY DIP
Previous: Signal/noise decomposition examples
Since signal and noise are uncorrelated,
the spectrum of data is the spectrum of the signal plus that of the noise.
An equation for this idea is
| 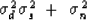 |
(15) |
This says resonances in the signal
and resonances in the noise
will both be found in the data.
When we are given 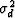 and
and 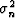 it seems a simple
matter to subtract to get
it seems a simple
matter to subtract to get 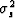 .Actually it can be very tricky.
We are never given
.Actually it can be very tricky.
We are never given 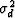 and
and 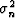 ;we must estimate them.
Further, they can be a function of frequency, wave number, or dip,
and these can be changing during measurements.
We could easily find ourselves with a negative estimate for
;we must estimate them.
Further, they can be a function of frequency, wave number, or dip,
and these can be changing during measurements.
We could easily find ourselves with a negative estimate for
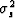 which would ruin any attempt to segregate signal from noise.
An idea of Simon Spitz can help here.
which would ruin any attempt to segregate signal from noise.
An idea of Simon Spitz can help here.
Let us reexpress equation (15) with prediction-error filters.
| 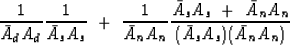 |
(16) |
Inverting
| 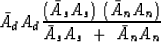 |
(17) |
The essential feature of a PEF is its zeros.
Where a PEF approaches zero, its inverse is large and resonating.
When we are concerned with the zeros of a mathematical function
we tend to focus on numerators and ignore denominators.
The zeros in
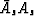 compound with the zeros in
compound with the zeros in
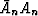 to make the zeros in
to make the zeros in
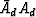 .This motivates the ``Spitz Approximation.''
.This motivates the ``Spitz Approximation.''
| 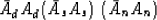 |
(18) |
It usually happens that we can
find a patch of data where no signal is present.
That's a good place to estimate the noise PEF An.
It is usually much harder to find a patch of data where no noise is present.
This motivates the Spitz approximation which by saying
Ad = As An
tells us that the hard-to-estimate As is the ratio
As = Ad / An
of two easy-to-estimate PEFs.
It would be computationally convenient if
we had As expressed not as a ratio.
For this, form the signal
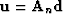 by applying the noise PEF An to the data
by applying the noise PEF An to the data 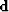 .The spectral relation is
.The spectral relation is
| 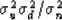 |
(19) |
Inverting this expression
and using the Spitz approximation
we see that
a PEF estimate on 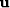 is the required As in numerator form because
is the required As in numerator form because
| 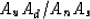 |
(20) |





Next: Noise removal on Shearer's
Up: SIGNAL-NOISE DECOMPOSITION BY DIP
Previous: Signal/noise decomposition examples
Stanford Exploration Project
4/27/2004
![]() by applying the noise PEF An to the data
by applying the noise PEF An to the data ![]() .The spectral relation is
.The spectral relation is