




Next: About this document ...
Up: Spectrum and phase
Previous: ROBINSON'S ENERGY-DELAY THEOREM
We have seen that in a cascade of filters
the Z-transform polynomials are multiplied together.
For
filters in parallel
the polynomials add.
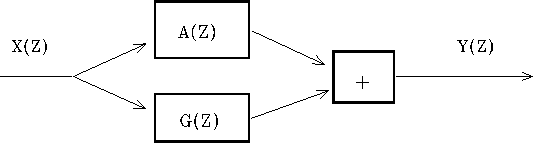
See Figure 21.
parallel
Figure 21
Filters operating in parallel.
|
|  |

We have seen also that a cascade of filters is minimum-phase if,
and only if,
each element of the product is minimum-phase.
Now we will find a condition that
is sufficient (but not necessary) for
a sum A(Z) + G(Z) to be minimum-phase.
First, assume that A(Z) is minimum-phase.
Then write
| 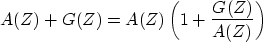 |
(40) |
The question as to whether A(Z) + G(Z) is minimum-phase
is now reduced to determining
whether A(Z) and 1 + G(Z)/A(Z) are both minimum-phase.
We have assumed that A(Z) is minimum-phase.
Before we ask whether 1 + G(Z)/A(Z) is minimum-phase,
we need to be sure that it is causal.
Since 1/A(Z) is expandable in positive powers of Z only,
then G(Z)/A(Z) is also causal.
We will next see that a sufficient condition for
1 + G(Z)/A(Z) to be minimum-phase is that
the spectrum of A exceed that of G at all frequencies.
In other words, for any real  , |A |> |G |.
Thus, if we plot the curve of G(Z)/A(Z) in the complex plane,
for real
, |A |> |G |.
Thus, if we plot the curve of G(Z)/A(Z) in the complex plane,
for real  ,it lies everywhere inside the unit circle.
Now, if we add unity, obtaining 1 + G(Z)/A(Z),
then the curve will always have a positive real part as in
Figure 22.
,it lies everywhere inside the unit circle.
Now, if we add unity, obtaining 1 + G(Z)/A(Z),
then the curve will always have a positive real part as in
Figure 22.
garbage
Figure 22
A phase trajectory as in Figure 18
left, but more complicated.
|
| 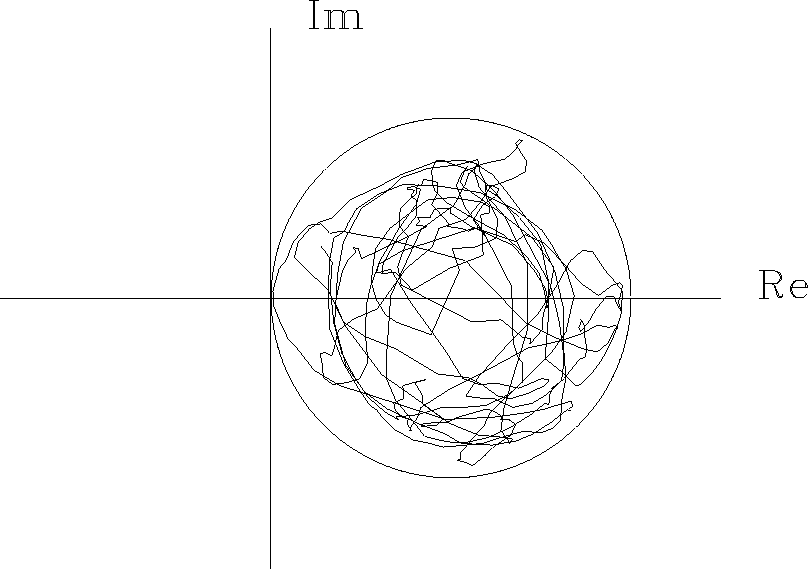 |





Since the curve cannot enclose the origin,
the phase must be that of a minimum-phase function.
|
You can add garbage to a minimum-phase wavelet
if you do not add too much.
|
This abstract theorem has an immediate physical consequence.
Suppose a wave characterized
by a minimum-phase A(Z) is emitted from a source and
detected at a receiver some time later.
At a still later time, an echo bounces off
a nearby object and is also detected at the receiver.
The receiver sees the signal
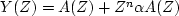 ,where n measures the delay from the first arrival
to the echo, and
,where n measures the delay from the first arrival
to the echo, and  represents the amplitude attenuation
of the echo.
To see that Y(Z) is minimum-phase,
we note that the magnitude of Zn
is unity and the reflection coefficient
represents the amplitude attenuation
of the echo.
To see that Y(Z) is minimum-phase,
we note that the magnitude of Zn
is unity and the reflection coefficient  must be less than unity
(to avoid perpetual motion),
so that
must be less than unity
(to avoid perpetual motion),
so that 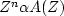 takes the role of G(Z).
Thus, a minimum-phase wave along with its echo is minimum-phase.
We will later consider wave propagation with echoes of echoes
ad infinitum.
takes the role of G(Z).
Thus, a minimum-phase wave along with its echo is minimum-phase.
We will later consider wave propagation with echoes of echoes
ad infinitum.
EXERCISES:
-
Find two nonminimum-phase wavelets whose sum is minimum-phase.
-
Let A(Z) be a minimum-phase polynomial of degree N.
Let
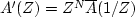 .Locate in the complex Z plane the roots of A'(Z).
A'(Z) is called ``maximum phase."
(HINT: Work the simple case A(Z) = a0 + a1Z first.)
.Locate in the complex Z plane the roots of A'(Z).
A'(Z) is called ``maximum phase."
(HINT: Work the simple case A(Z) = a0 + a1Z first.)
-
Suppose that A(Z) is maximum-phase and that the degree of G(Z) is less
than or equal to the degree of A(Z). Assume |A|>|G|.
Show that A(Z) + G(Z) is maximum-phase.
-
Let A(Z) be minimum-phase.
Where are the roots of
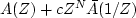 in the three cases
| c | < 1, | c | > 1, | c | = 1?
(HINT: The roots of a polynomial are continuous functions of the
polynomial coefficients.)
in the three cases
| c | < 1, | c | > 1, | c | = 1?
(HINT: The roots of a polynomial are continuous functions of the
polynomial coefficients.)





Next: About this document ...
Up: Spectrum and phase
Previous: ROBINSON'S ENERGY-DELAY THEOREM
Stanford Exploration Project
10/21/1998



![]() ,where n measures the delay from the first arrival
to the echo, and
,where n measures the delay from the first arrival
to the echo, and ![]() represents the amplitude attenuation
of the echo.
To see that Y(Z) is minimum-phase,
we note that the magnitude of Zn
is unity and the reflection coefficient
represents the amplitude attenuation
of the echo.
To see that Y(Z) is minimum-phase,
we note that the magnitude of Zn
is unity and the reflection coefficient ![]() must be less than unity
(to avoid perpetual motion),
so that
must be less than unity
(to avoid perpetual motion),
so that ![]() takes the role of G(Z).
Thus, a minimum-phase wave along with its echo is minimum-phase.
We will later consider wave propagation with echoes of echoes
ad infinitum.
takes the role of G(Z).
Thus, a minimum-phase wave along with its echo is minimum-phase.
We will later consider wave propagation with echoes of echoes
ad infinitum.