 |
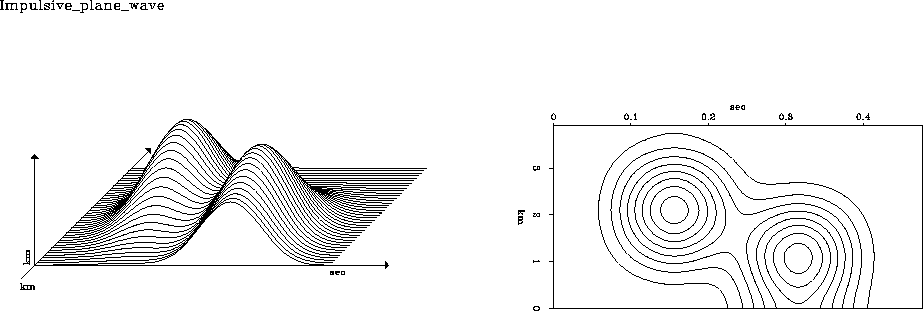
Figure 12 Two impulses in two dimensions filtered twice on each axis with a triangle function. Left: bird's-eye view. Right: contours of constant altitude z.
 |
Notice that the contours, instead of being diamonds and rectangles,
have become much more circular.
The reason for this is briefly as follows:
convolution of a rectangle with itself many times
approachs the limit of a Gaussian function.
(This is a well-known result called the
``central-limit theorem.''
It is explained in section ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) .)
It happens that the convolution of a triangle with itself
is already a good approximation to the Gaussian function
z(x)= e-x2.
The convolution in y gives z(x,y)=e-x2-y2= e-r2,
where r is the radius of the circle.
When the triangle on the 1-axis differs in width
from the triangle on the 2-axis,
then the circles become ellipses.
.)
It happens that the convolution of a triangle with itself
is already a good approximation to the Gaussian function
z(x)= e-x2.
The convolution in y gives z(x,y)=e-x2-y2= e-r2,
where r is the radius of the circle.
When the triangle on the 1-axis differs in width
from the triangle on the 2-axis,
then the circles become ellipses.