




Next: Probability and independence
Up: TIME-STATISTICAL RESOLUTION
Previous: Ensemble
A conceptual average over the ensemble,
or expectation,
is denoted by the symbol 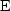 .The index for summation over the ensemble is never shown explicitly;
every random variable is presumed to have one.
Thus, the true mean at time t is defined as
.The index for summation over the ensemble is never shown explicitly;
every random variable is presumed to have one.
Thus, the true mean at time t is defined as 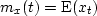 .The mean can vary with time:
.The mean can vary with time:
| ![\begin{displaymath}
m_x(t) \eq \E[x(t)]\end{displaymath}](img48.gif) |
(12) |
The ``variance'' 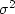 is defined to be the power after the mean is removed, i.e.,
is defined to be the power after the mean is removed, i.e.,
| ![\begin{displaymath}
\sigma_x(t)^2 \eq \E\, [(x(t) - m_x(t))^2]\end{displaymath}](img50.gif) |
(13) |
(Conventionally, 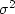 is referred to as the variance,
and
is referred to as the variance,
and  is called the
``standard deviation.'')
is called the
``standard deviation.'')
For notational convenience, it is customary to write
m(t), 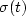 , and x(t) simply as
m,
, and x(t) simply as
m,  , and xt,
using the verbal context to specify whether
m and
, and xt,
using the verbal context to specify whether
m and  are time-variable or constant.
For example, the standard deviation of the seismic
amplitudes on a seismic trace before correction of spherical
divergence decreases with time, since these amplitudes are expected
to be ``globally'' smaller as time goes on.
are time-variable or constant.
For example, the standard deviation of the seismic
amplitudes on a seismic trace before correction of spherical
divergence decreases with time, since these amplitudes are expected
to be ``globally'' smaller as time goes on.
When manipulating algebraic expressions, remember that
the symbol 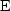 behaves like a summation sign, namely,
behaves like a summation sign, namely,
| 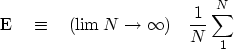 |
(14) |
Note that the summation index is not given,
since the sum is over the ensemble, not time.
To get some practice with the expectation symbol 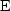 , we
can reduce equation (13):
, we
can reduce equation (13):
| ![\begin{displaymath}
\sigma_x^2
\eq \E\, [(x_t - m_x)^2]
\eq \E(x_t^2) \ - \ 2 m_x \E(x_t) + m_x^2
\eq \E(x_t^2) \ - \ m_x^2\end{displaymath}](img54.gif) |
(15) |
Equation (15)
says that the energy is the variance plus the squared mean.





Next: Probability and independence
Up: TIME-STATISTICAL RESOLUTION
Previous: Ensemble
Stanford Exploration Project
10/21/1998
![]() , and x(t) simply as
m,
, and x(t) simply as
m, ![]() , and xt,
using the verbal context to specify whether
m and
, and xt,
using the verbal context to specify whether
m and ![]() are time-variable or constant.
For example, the standard deviation of the seismic
amplitudes on a seismic trace before correction of spherical
divergence decreases with time, since these amplitudes are expected
to be ``globally'' smaller as time goes on.
are time-variable or constant.
For example, the standard deviation of the seismic
amplitudes on a seismic trace before correction of spherical
divergence decreases with time, since these amplitudes are expected
to be ``globally'' smaller as time goes on.
![]() behaves like a summation sign, namely,
behaves like a summation sign, namely,