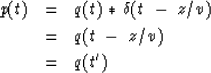Next: Einstein's special relativity theory
Up: RETARDED COORDINATES
Previous: Fourier transforms in retarded
Earlier a variable Q was defined from the pressure P by the equation
| ![\begin{displaymath}
P( \omega ) \eq Q( \omega )\
\exp \left[ \ i \omega \int_0^z {dz \over \bar v (z)} \ \right]\end{displaymath}](img92.gif) |
(42) |
The right side is a product of two functions of 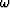 .At constant velocity (42) is expressed as
.At constant velocity (42) is expressed as
| 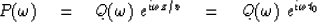 |
(43) |
In the time domain 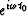 becomes a delta function
becomes a delta function 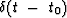 .Equation (43) is a product in the frequency domain,
so in the time domain it is the convolution
.Equation (43) is a product in the frequency domain,
so in the time domain it is the convolution
| 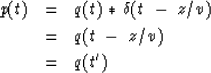 |
|
| |
| (44) |
This confirms that the definition of a
dependent variable Q is equivalent
to introducing retarded time t'.





Next: Einstein's special relativity theory
Up: RETARDED COORDINATES
Previous: Fourier transforms in retarded
Stanford Exploration Project
10/31/1997