




Next: Tal-Ezer Method
Up: THE GENERALIZED PHASE-SHIFT METHOD
Previous: Horizontally Uniform Structures
When the velocity structure varies in the lateral direction, the Fourier
transform of velocity is no longer a delta function and the submatrix
A21 has the form
| ![\begin{displaymath}[A_{21}]
=\pmatrix{-{\omega^2 s_0}+k_x^2 & -\omega^2 s_1 & \l...
...x-1} & -\omega^2 s_{N_x-2} & \ldots & -{\omega^2s_0}+k_x^2 \cr}\end{displaymath}](img24.gif) |
(15) |
where
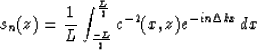
Another derivation of submatrix A21 is possible in space frequency domain
(Kosloff and Kessler, 1987). Whether the derivative in equation (6) is
calculated by the Fourier method as with the ordinary phase-shift method
(Gazdag, 1978), or by finite differences with periodic horizontal boundary
conditions, it can be written as the cyclic convolution
| 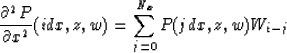 |
(16) |
where Wi denotes a convolution operator.
For example, for second-order finite differences, 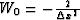 and
and 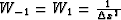 , and Wi=0 for |i|>1. For Fourier
second-derivative operator,
, and Wi=0 for |i|>1. For Fourier
second-derivative operator,
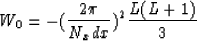
and
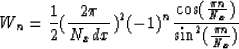
with Nx=2L+1(Kosloff and Kessler, 1987).
With the spatial discretization and specification of the second-derivative
approximation, the elements of the Nx by Nx submatrix A21 are
given by
| ![\begin{displaymath}[A_{21}]
=\pmatrix{-{\omega^2 \over c_1^2}-W_0 & -W_1 & \ldot...
...{x-1}} & -W_{N_{x-2}} & \ldots &-{\omega^2\over c_{N_x}^2}-W_0}\end{displaymath}](img31.gif) |
(17) |
where ci=c(idx,z)





Next: Tal-Ezer Method
Up: THE GENERALIZED PHASE-SHIFT METHOD
Previous: Horizontally Uniform Structures
Stanford Exploration Project
1/13/1998
![\begin{displaymath}[A_{21}]
=\pmatrix{-{\omega^2 s_0}+k_x^2 & -\omega^2 s_1 & \l...
...x-1} & -\omega^2 s_{N_x-2} & \ldots & -{\omega^2s_0}+k_x^2 \cr}\end{displaymath}](img24.gif)
![\begin{displaymath}[A_{21}]
=\pmatrix{-{\omega^2 s_0}+k_x^2 & -\omega^2 s_1 & \l...
...x-1} & -\omega^2 s_{N_x-2} & \ldots & -{\omega^2s_0}+k_x^2 \cr}\end{displaymath}](img24.gif)
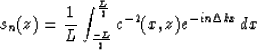
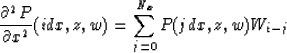
![]()
![]()
![\begin{displaymath}[A_{21}]
=\pmatrix{-{\omega^2 \over c_1^2}-W_0 & -W_1 & \ldot...
...{x-1}} & -W_{N_{x-2}} & \ldots &-{\omega^2\over c_{N_x}^2}-W_0}\end{displaymath}](img31.gif)