Next: Results
Up: Curry: Interpolation with pseudo-primariesPseudo-primary
Previous: Generation of pseudo-primaries
Interpolation can be cast as a series of two inverse problems where a prediction-error
filter is estimated on known data and is then used to interpolate
missing data. A prediction-error filter (PEF) can be estimated by
minimizing the output of convolution of known data with an unknown
filter (except for the leading 1), which can be written in matrix form
as
| ![\begin{displaymath}
\bold 0
\quad \approx \quad
\bold r =
\left[
\begin{array}
{...
...
{c}
d_2 \ d_3 \ d_4 \ d_5 \ d_6 \end{array} \right]
,\end{displaymath}](img4.gif) |
(2) |
where fi are unknown filter values and di are known data values.
The filters used in this paper are all multidimensional, which are
computed with the helical coordinate. In the case of
a stationary multidimensional PEF, this is an over-determined
least-squares problem with a unique solution.
Seismic data is non-stationary in nature, so a single stationary PEF is
not adequate for the many changing dips present. We estimate a single
spatially-variable nonstationary PEF and solve a global optimization
problem Guitton (2003). In that case the problem is now
under-determined, and a regularization operator is introduced to the
least-squares problem (in matrix notation) so that,
| 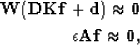 |
|
| (3) |
where 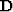 represents non-stationary convolution with the data,
represents non-stationary convolution with the data, 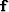 is now a
non-stationary PEF,
is now a
non-stationary PEF, 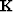 (a selector matrix) and
(a selector matrix) and 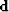 (a copy of the data)
both constrain the value of the first filter coefficient to 1,
(a copy of the data)
both constrain the value of the first filter coefficient to 1, 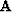 is a
regularization operator (a Laplacian operating over space) and
is a
regularization operator (a Laplacian operating over space) and  is a
trade-off parameter for the regularization. Solving this system will
create a smoothly non-stationary PEF.
is a
trade-off parameter for the regularization. Solving this system will
create a smoothly non-stationary PEF.
Once the PEF has been estimated, it can be used in a second least
squares problem that matches the output model to the known data while
simultaneously regularizing the model with the newly found PEF,
| 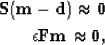 |
|
| (4) |
where 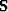 is a selector matrix which is 1 where data
is present and where it is not,
is a selector matrix which is 1 where data
is present and where it is not, 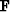 represents convolution with the
non-stationary PEF,
represents convolution with the
non-stationary PEF,  is now a trade-off parameter and
is now a trade-off parameter and 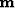 is the desired
model.
interped
is the desired
model.
interped
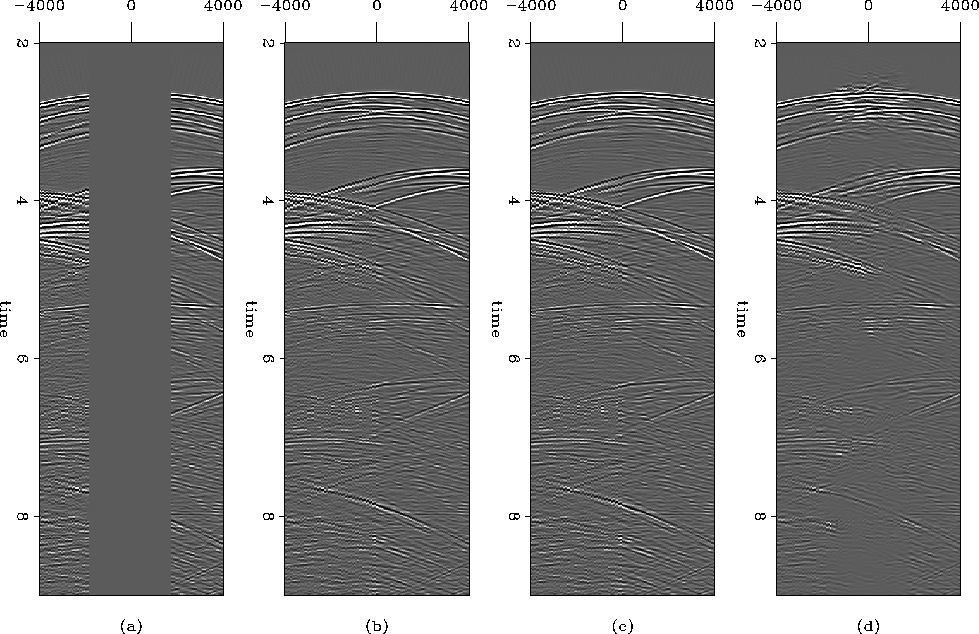
Figure 2 (a) Original data with near offsets (<2000 feet) missing. (b)
Original complete data. (c) Interpolation with PEF based upon complete
data. (d) Interpolation with PEF based upon pseudo-primaries.










Next: Results
Up: Curry: Interpolation with pseudo-primariesPseudo-primary
Previous: Generation of pseudo-primaries
Stanford Exploration Project
4/5/2006
![\begin{displaymath}
\bold 0
\quad \approx \quad
\bold r =
\left[
\begin{array}
{...
...
{c}
d_2 \ d_3 \ d_4 \ d_5 \ d_6 \end{array} \right]
,\end{displaymath}](img4.gif)
![\begin{displaymath}
\bold 0
\quad \approx \quad
\bold r =
\left[
\begin{array}
{...
...
{c}
d_2 \ d_3 \ d_4 \ d_5 \ d_6 \end{array} \right]
,\end{displaymath}](img4.gif)