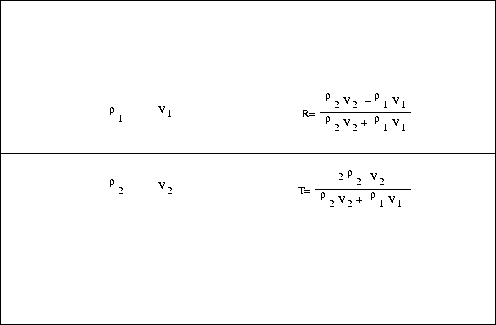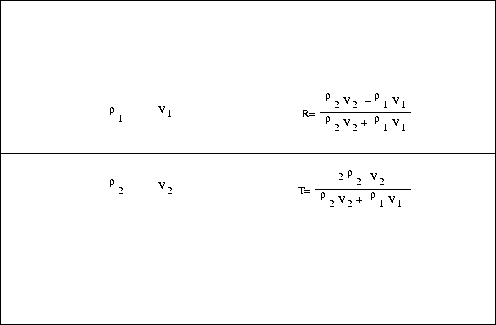Next: Iterative inversion imaging algorithms
Up: wave propagator and its
Previous: [2] Scalar wave equation
reflectivity
Figure 1 The acoustic wave reflectivity and the transmission of a planar reflector in the case of zero incident angle





From Fig.1, and assuming that the density is constant, the normal reflectivity is defined as
| 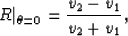 |
(16) |
and the transmission coefficient is
| 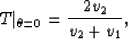 |
(17) |
where 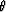 is the incident angle. Therefore, defining the scattering potential as
is the incident angle. Therefore, defining the scattering potential as 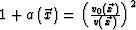 , equation (16) and (17) can be rewritten as
, equation (16) and (17) can be rewritten as
| 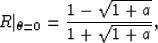 |
(18) |
and
| 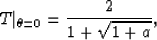 |
(19) |
respectively.
If waves meet a reflector with a non-zero incident angle, the reflectivity and transmission coefficient are
| 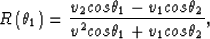 |
(20) |
and
| 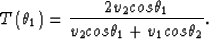 |
(21) |
Similarly, they can be expressed with the scattering potential as
| 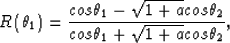 |
(22) |
and
| 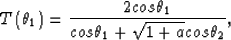 |
(23) |
respectively.
The angle reflectivity has a close relation to the scattering potentials. Generally, the angle reflectivity is estimated by amplitude-preserved imaging, and lithological parameter disturbances are evaluated from them by AVO/AVA inversion.





Next: Iterative inversion imaging algorithms
Up: wave propagator and its
Previous: [2] Scalar wave equation
Stanford Exploration Project
11/1/2005