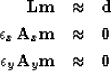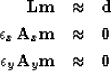Next: Tests
Up: Brown: Irregular data dip
Previous: Irregular-geometry Dip Estimation Methodology
In least-squares fitting goals, the regularized inverse interpolation problem
can be stated as follows:
| 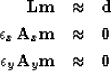 |
(7) |
| (8) |
| (9) |
Operator 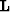 maps traces in a gridded model
maps traces in a gridded model 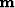 to the earth's
continuous surface. Operators
to the earth's
continuous surface. Operators 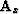 and
and 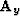 are ``steering
filters'' Clapp et al. (1997) in the x and y direction, respectively.
The steering filters are initialized with a space-variable dip function and
decorrelate events which have that dip, and tend to steer the estimated model
along the dip direction. In this fashion we impose our prior model covariance
estimate on the missing traces. Scalars
are ``steering
filters'' Clapp et al. (1997) in the x and y direction, respectively.
The steering filters are initialized with a space-variable dip function and
decorrelate events which have that dip, and tend to steer the estimated model
along the dip direction. In this fashion we impose our prior model covariance
estimate on the missing traces. Scalars 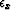 and
and 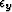 balance
the two model residuals [equations (8) and (9)] with
the data residual [equation (7)].
balance
the two model residuals [equations (8) and (9)] with
the data residual [equation (7)].





Next: Tests
Up: Brown: Irregular data dip
Previous: Irregular-geometry Dip Estimation Methodology
Stanford Exploration Project
10/14/2003