Next: Discussion
Up: From the filtering to
Previous: The filtering method
There is a simple trick that modifies the fitting goals in equation (2).
We can pose the following preconditioning transformations:
| 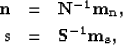 |
|
| (4) |
where 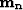 and
and 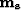 are new variables.
Now we can derive a new system of fitting goals as follows:
are new variables.
Now we can derive a new system of fitting goals as follows:
| 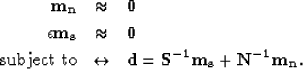 |
|
| (5) |
| |
This system is almost equivalent to what I introduced in
Guitton (2001), except for the regularization
that I omitted. With 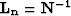 the noise-modeling operator and
the noise-modeling operator and 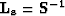 the signal-modeling
operator, the least-squares inverse of
equations (5) without the regularization terms is then given by
with
the signal-modeling
operator, the least-squares inverse of
equations (5) without the regularization terms is then given by
with
| 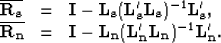 |
(6) |
I showed in Guitton et al. (2001) that 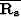 and
and
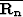 can also be interpreted in term of projection
filters.
can also be interpreted in term of projection
filters.
The estimated noise and signal are then computed as follows
| 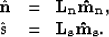 |
(7) |
Because of the relationship that exists between the filtering and
subtraction methods, the estimated noise or signal should be equivalent
for both. This has been observed in a multiple attenuation problem by
Guitton et al. (2001).





Next: Discussion
Up: From the filtering to
Previous: The filtering method
Stanford Exploration Project
6/7/2002