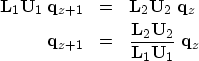Next: Impulse response
Up: Helical boundary conditions
Previous: Cross-spectral factorization
Kolmogoroff cross-spectral factorization, therefore, provides a tool
to factor the helical 1-D filter of length 2Nx + 1 into
minimum-phase causal and anti-causal filters of length Nx +1.
Fortunately, filter coefficients drop away rapidly from either end.
In practice, small-valued coefficients can be safely discarded,
without violating the minimum-phase requirement; so for a
given grid-size, the cost of the matrix inversion scales linearly with
the size of the grid.
The unitary form of equation (3) can be maintained
by factoring the right-hand-side matrix,
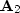 in equation (6), with Kolmogoroff before
applying it to
in equation (6), with Kolmogoroff before
applying it to 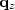 .
.
| 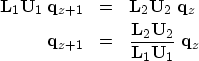 |
(11) |
| (12) |





Next: Impulse response
Up: Helical boundary conditions
Previous: Cross-spectral factorization
Stanford Exploration Project
7/5/1998
![]() in equation (6), with Kolmogoroff before
applying it to
in equation (6), with Kolmogoroff before
applying it to ![]() .
.