Next: RESULTS
Up: Rickett, Biondi & Lumley:
Previous: METHOD
Quantitative studies of the validity of first Born approximation have
been made by various authors Beydoun and Tarantola (88); Hudson and Heritage (81); Malin and Phinney (1985), but we need
to have a feel for the accuracy we may expect given the amplitude
of the perturbations we have in our case.
To do this, results of the scattering method were compared with plane wave
reflection coefficients calculated using Zoeppritz equations.
The first set of models tested in this way were the three
interfaces described by Rutherford and Williams 1989.
These correspond to a variety of different shale/gas-sand AVO signatures.
The relevant medium parameters are shown in Table 1, and the changes in
elastic parameters across the interface are comparable with our case.
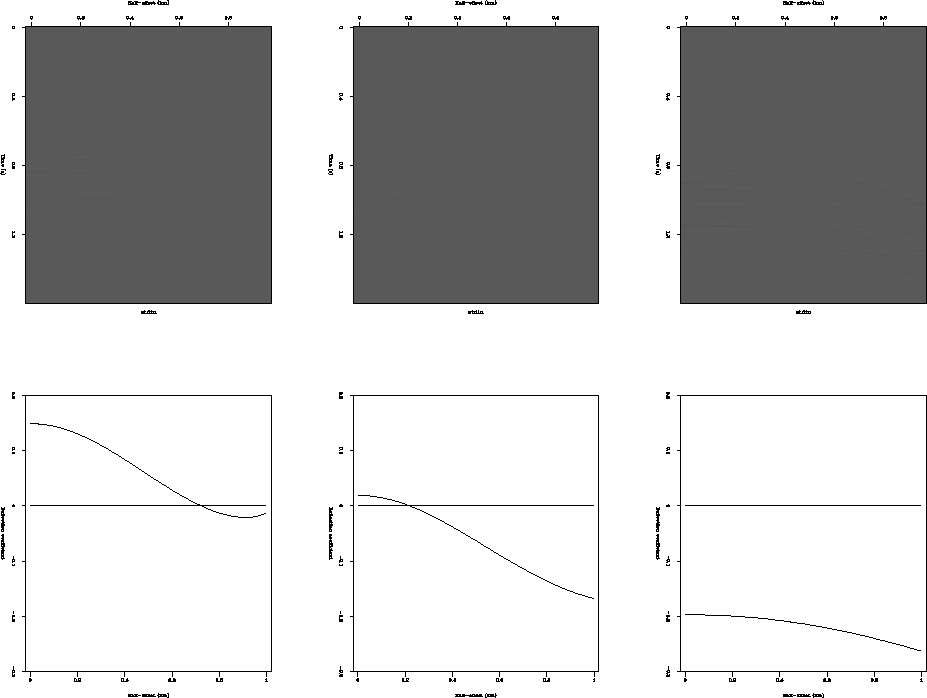
Figure 1 shows the results of modeling these interfaces. The upper
panels show results of Born modeling of a layer 1 km deep; corrections
have been made for geometrical spreading and geophone directionality. The
lower panels show the reflection coefficients for the same interfaces.
The horizontal axes are half-offset in both cases, so comparisons can be made.
rw
Figure 1
The upper panels show results of Born modeling of interfaces at
1 km depth; corrections
have been made for geometrical spreading and geophone directionality. The
lower panels show the Zoeppritz
reflection coefficients for the same interfaces.
The horizontal axes are half-offset in both cases. Left panels are for a
Class 1 interface, center panels are for a Class 2 interface and right panels
are for a Class 3 interface.





The two modeling techniques are based upon totally different assumptions -
Zoeppritz matches plane wave boundary conditions across a plane interface,
and Born treats the interface as a series of independent
weak scatterers: therefore it would be unrealistic the results to be in
exact agreement. However, despite this, they show very
good qualitative agreement: the phases are all correct, the phase
reversals happen all at approximately the right offset, and the amplitudes
increase or decrease in the right way. The choice to display one set of results
as raster plots and the second set of results as graphs was made to emphasize
that we were not expecting perfect agreement.
The second set of interfaces that were tested corresponded to boundaries
between lithologies used in the reservoir modeling project. This gave
understanding of the levels of accuracy we obtained for our
seismic modeling, and it also provides insight into AVO signatures we may
expect when analyzing the results.
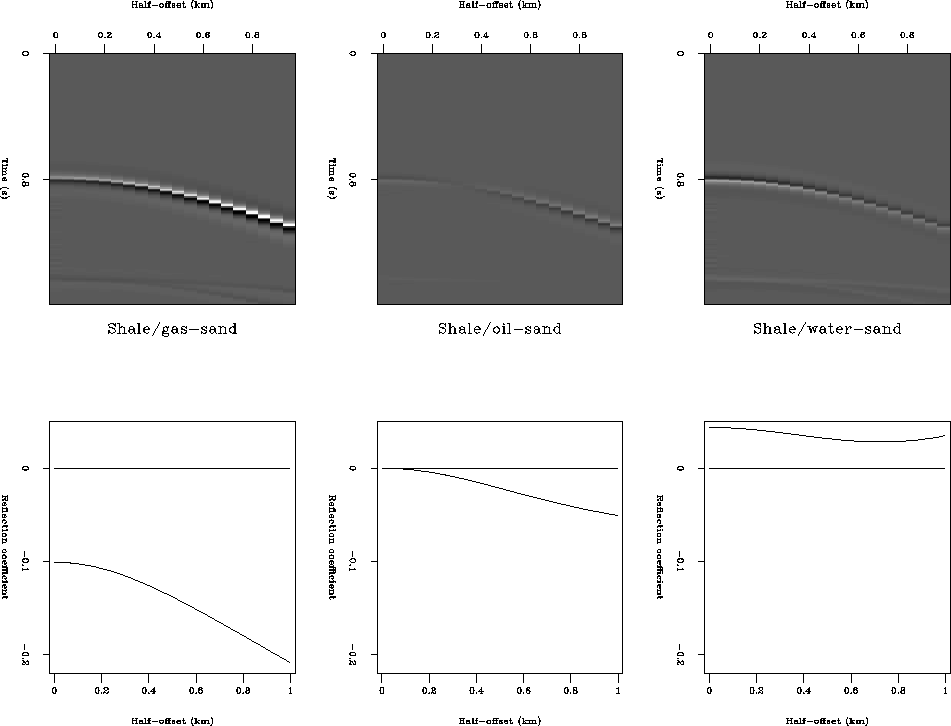
Figure 2 shows Born modeling and Zoeppritz reflection coefficients
for shale/gas-sand, shale/oil-sand and shale/water-sand contacts with
elastic parameters taken from Biondi et al.1996.
The same corrections have been
applied as in Figure 1 to facilitate qualitative comparison.
Again the two modeling techniques give good agreement.
geope
Figure 2
The upper panels show results of Born modeling of interfaces at
1 km depth; corrections
have been made for geometrical spreading and geophone directionality. The
lower panels show the reflection coefficients for the same interfaces.
The horizontal axes are half-offset in both cases. Left panels are for a
shale/gas-sand interface, center panels are for a shale/oil-sand interface
and right panels are for a shale/water-sand interface.





Both the shale/oil-sand and shale/gas-sand interfaces show increasing
reflection coefficient with angle; but as could be expected, this effect
is significantly larger for the shale/gas-sand interface.





Next: RESULTS
Up: Rickett, Biondi & Lumley:
Previous: METHOD
Stanford Exploration Project
11/12/1997