|
|
|
|
Modeling, migration, and inversion in the generalized source and receiver domain |
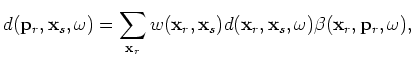 is the receiver phase-encoding function.
Equation 17 integrates along the vertical dashed lines shown in Figure 1 for each source location
is the receiver phase-encoding function.
Equation 17 integrates along the vertical dashed lines shown in Figure 1 for each source location 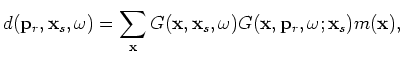 is the encoded receiver Green's function defined as follows:
is the encoded receiver Green's function defined as follows:
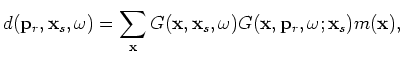 depends on
depends on
We minimize the following objective function in the encoded receiver domain (see Appendix B for derivation):
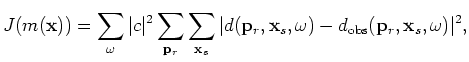 |
(A-23) |
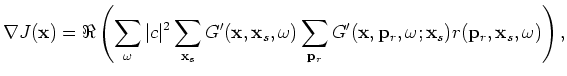 is defined as follows:
is defined as follows:
| (A-24) |
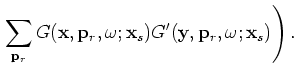 |
(A-26) |
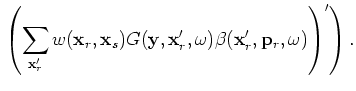 and B-
and B-
|
|
|
|
Modeling, migration, and inversion in the generalized source and receiver domain |