| |
(1) |
Thus if the total amount of strain, ![]() , is different for tests in
which the residence time of the stress,
, is different for tests in
which the residence time of the stress, ![]() , varies we will
measure a suite of compaction coefficients depending on our test
parameters rather than inherent properties of the rock. Intuitively,
we would expect this to happen; surely holding pressure constant for a longer
period of time will result in more compaction.
, varies we will
measure a suite of compaction coefficients depending on our test
parameters rather than inherent properties of the rock. Intuitively,
we would expect this to happen; surely holding pressure constant for a longer
period of time will result in more compaction.
To investigate this problem, several uniaxial strain experiments were measured by Dudley and Myers (1994) by increasing axial stress and holding for 1.5 hours, 1 day, 1 week and 1 year. The three shorter duration tests were repeated for 12 stress and hold cycles, while the year-long experiment was only conducted once. Figure 1 shows three such tests with 750 psi stress step. All samples are brine saturated and allow fluid to flow out of the sample with applied stress.
|
creep
Figure 1 Apparently unrelated stress-strain behavior of samples to uniaxial strain experiment.Dudley and Myers (1994) | 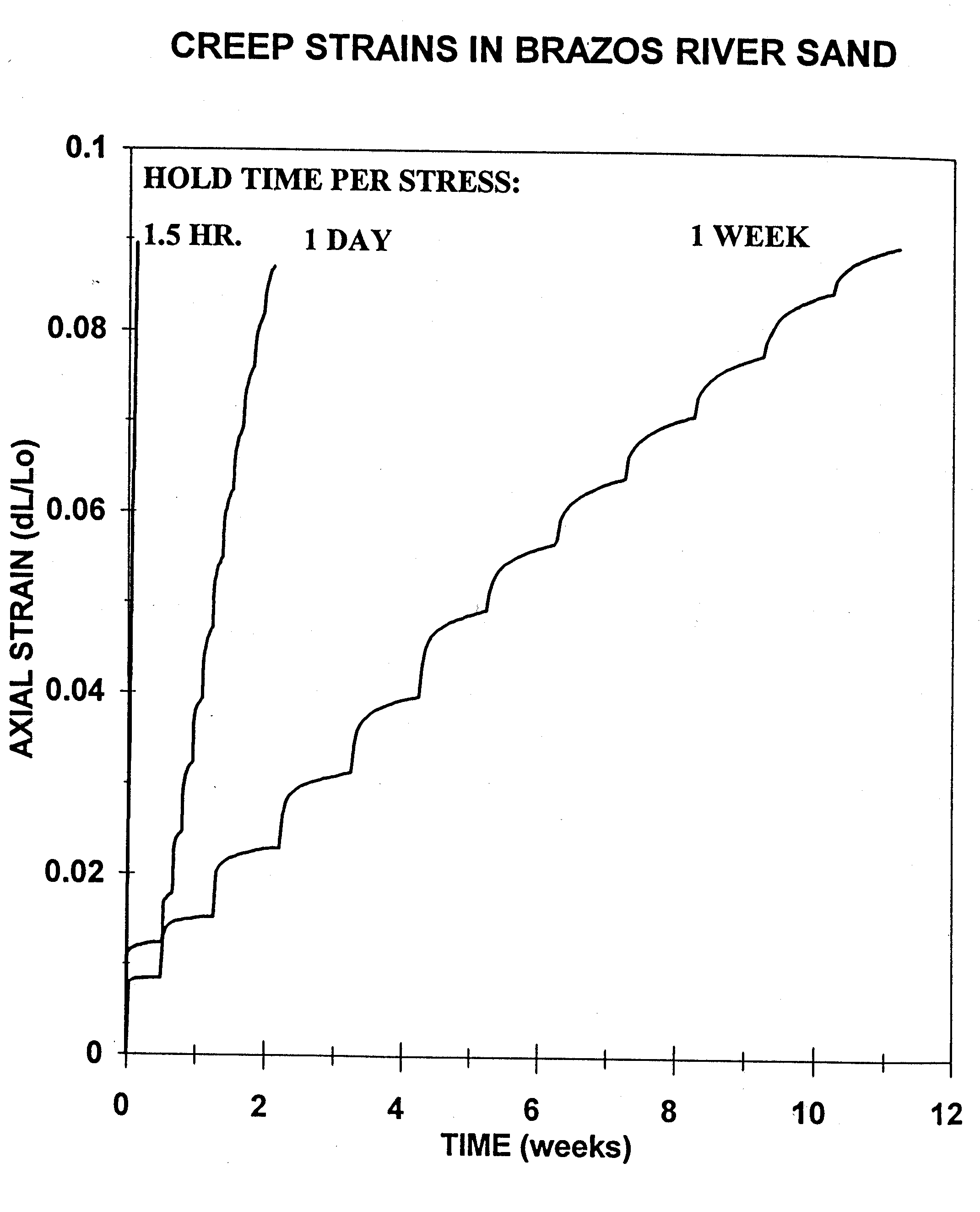 |
Figure 2 shows an example of the raw data from one stress cycle. Notice the extraordinary fit of the exponential curve to the integrated strain measurements over time. Figure 3 shows the surprising fact that by simply normalizing the time axis by the length of the hold time, the creep graphs all become coincident. This means that creep rate for longer experiments is slower than that for shorter experiments. This is simply amazing.
|
raw
Figure 2 24 hour hold time test for cycle to 8500 psi. Exponential fit of the form | 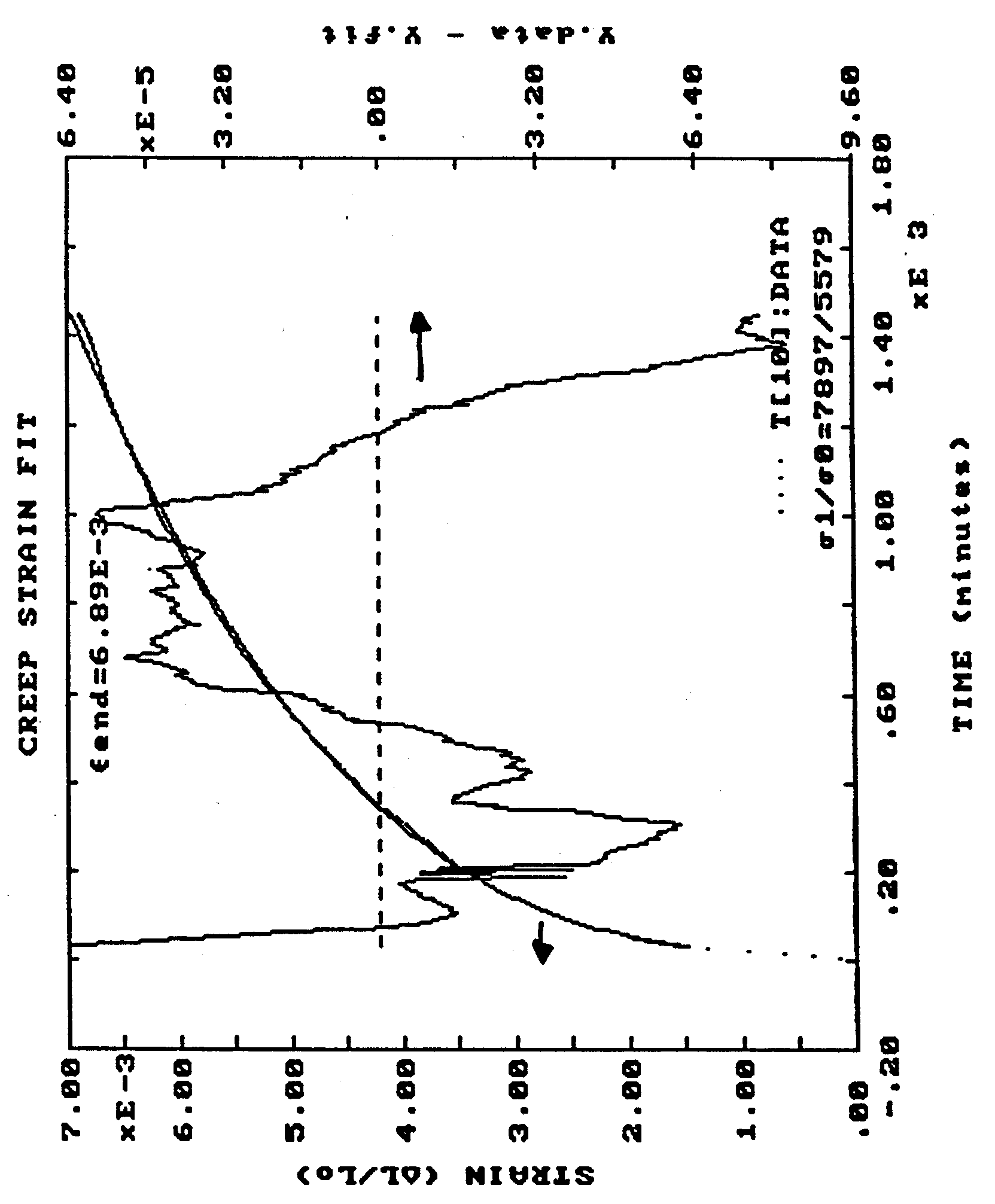 |
|
norm
Figure 3 Amazingly, all three tests show the same exponential increase of strain as a function of normalized time. More important: all tests attain the same final strain value despite two orders of magnitude difference in residence time. Mismatch of 1.5 hour test assumed to be a result of time for 750 psi pressure ramp-up being a significant (13%) portion of total hold time.Dudley and Myers (1994) | 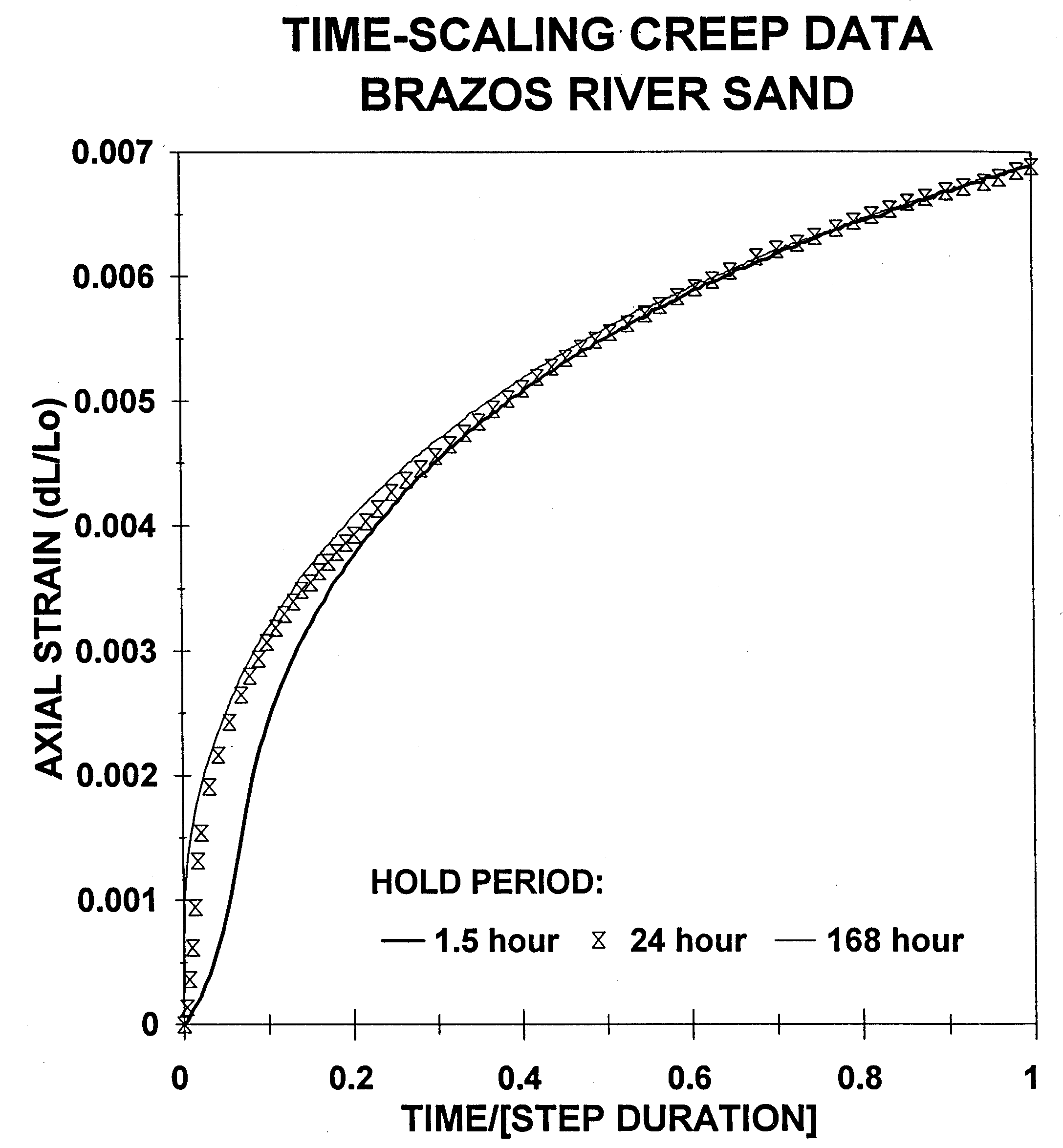 |
Several unsettling problems arise from these observations: