|
cup
Figure 1 Reflector model for the constant-velocity test |  |
|
cup
Figure 1 Reflector model for the constant-velocity test |  |
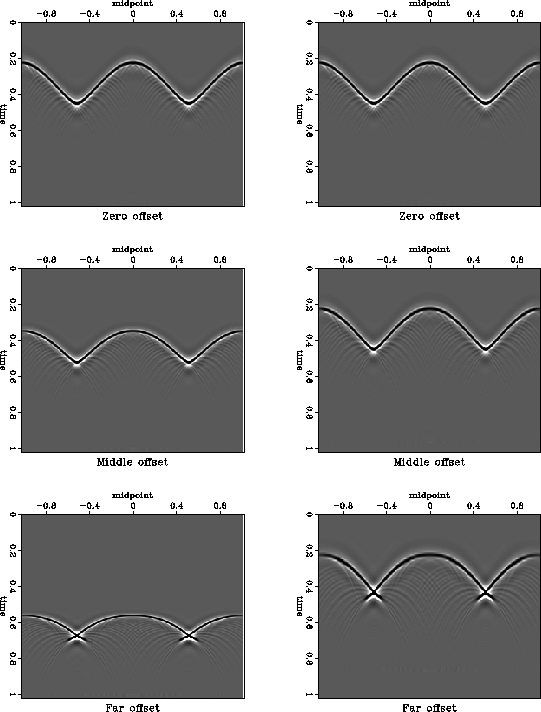
A sinusoidal reflector shown in Figure 1 creates complicated reflection data, shown in Figure 2 before and after the normal-moveout correction. The syncline parts of the reflector lead to traveltime triplications at sufficiently large offset. A mixture of different dips from the triplications would make it extremely difficult to interpolate the data in individual common-offset gathers, such as those shown in Figure 2. The plots of time slices after NMO (Figure 3) clearly show that the data are also non-stationary in the offset direction. Therefore, a simple offset interpolation scheme would also fail.
 |
![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/movie.gif)
 |
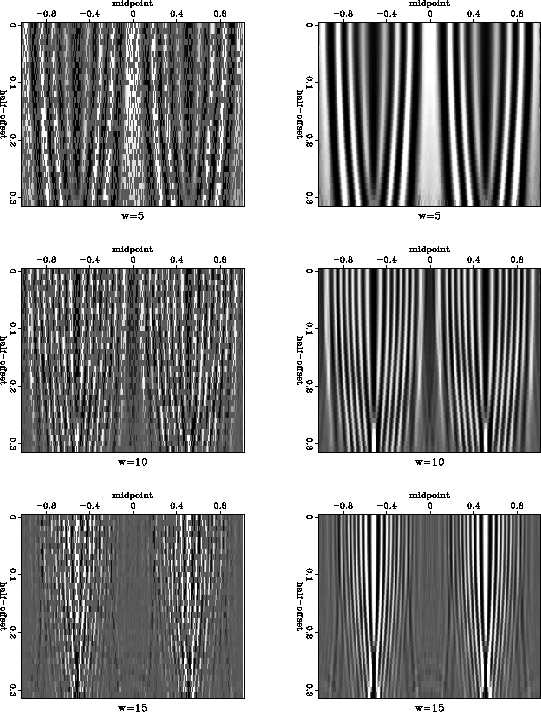
To set up an interpolation experiment, I randomly removed half of the traces in the original data and attempted to reconstruct them. Figure 4 shows the reconstruction process on individual frequency slices. Despite the complex and non-stationary character of the reflection events in the frequency domain, the offset continuation equation is able to reconstruct them quite accurately from the decimated data.
 |
![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/movie.gif)
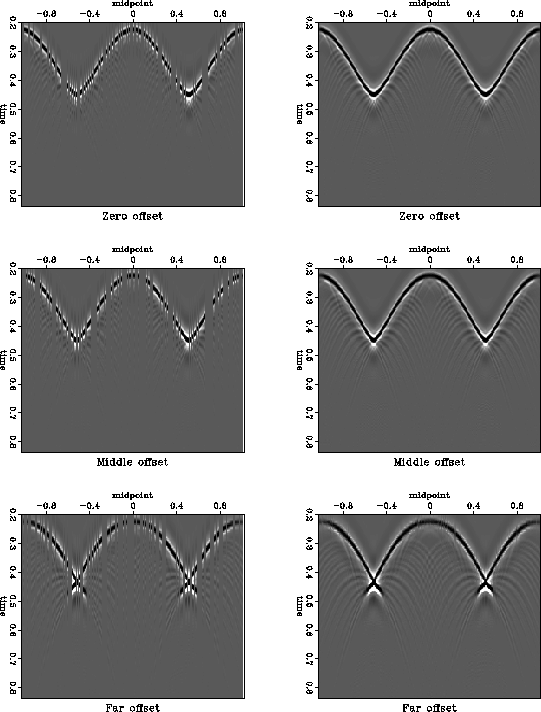
Figure 5 shows the input and the result of interpolation after transforming it back to the time domain. A comparison of the interpolation result with the ideal output (Figure 2) shows that the reflection data are nearly perfectly interpolated even in the complex triplication zones.
 |
![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/movie.gif)
The constant-velocity test results allow us to conclude that, when all the assumptions of the offset continuation theory are met, we can easily accomplish an accurate interpolation. In the next subsection, I deal with the more complicated case of Marmousi.