Next: Angle-domain CIG and AVA
Up: Angle-domain CIG by wave-equation
Previous: Angle-domain CIG by wave-equation
Angle-domain CIGs can be used to update the velocity function
after migration similarly to the way
that offset-domain CIGs are currently used
Brandsberg-Dahl et al. (1999) or for wave-equation Migration Velocity Analysis
Biondi and Sava (1999).
As for offset-domain CIGs, if the velocity function is
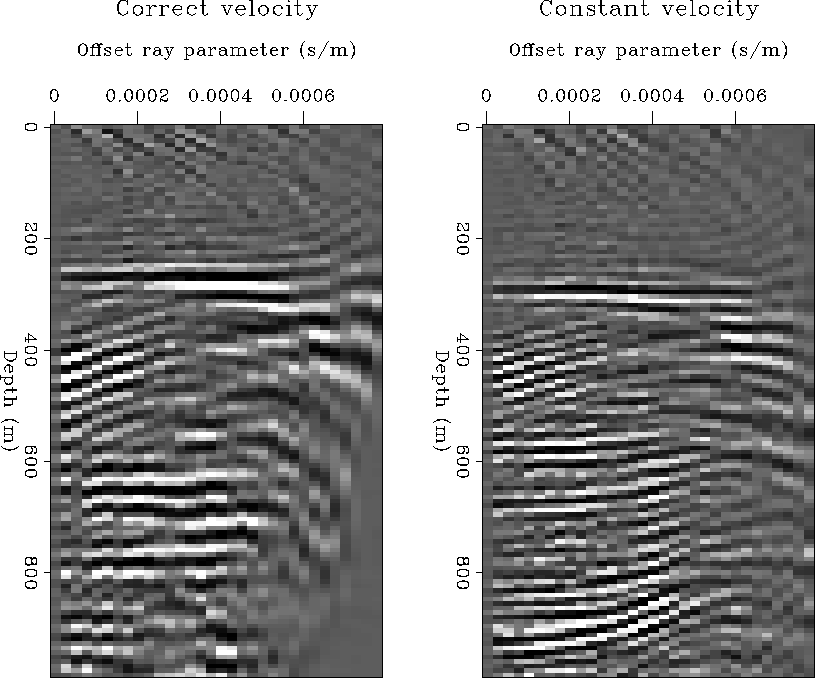
correct the reflections are aligned along the angle axis.
If the velocity function is too low the reflections
will smile upward;
if the velocity function is too high the reflections
will frown downward.
This behavior is demonstrated by the analysis
of the gathers in
Figure 6.
The gathers were extracted from a 3-D prestack wavefield
focused using common-azimuth downward continuation.
The left gather was obtained using the correct velocity.
The right gather was obtained using a low constant velocity.
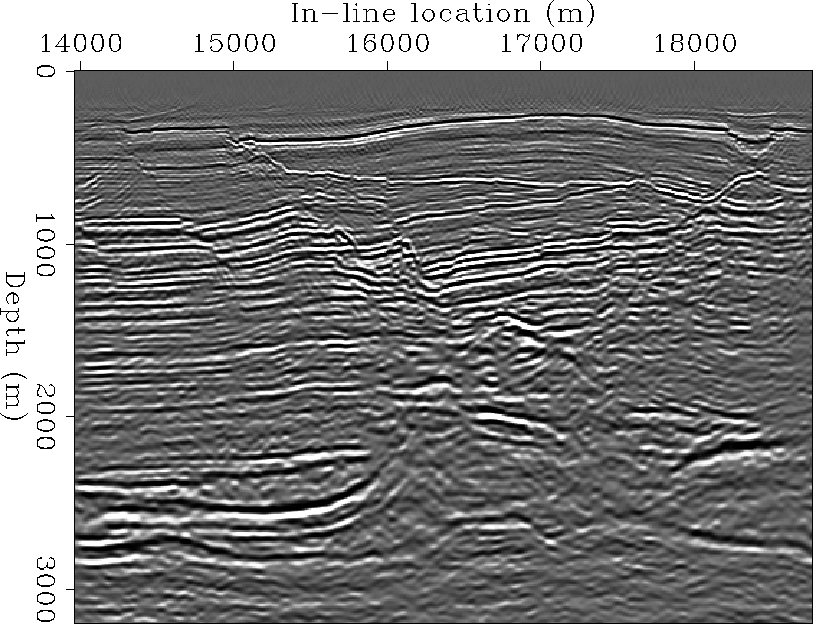
Figure 7 shows the inline migrated section
that passes through the gather shown in Figure 6.
Notice that the CIG gathers show only the first kilometer of the image.
AVO-jupiter-16801
Figure 6 Left: Angle-domain CIG with correct velocity. Right: Angle-domain CIG with too low constant velocity.




 Wave-jupiter-y20000
Wave-jupiter-y20000
Figure 7 In-line section of 3-D migrated cube










Next: Angle-domain CIG and AVA
Up: Angle-domain CIG by wave-equation
Previous: Angle-domain CIG by wave-equation
Stanford Exploration Project
4/20/1999