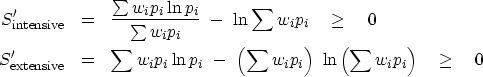Next: RELATED CONCEPTS
Up: THE JENSEN INEQUALITY
Previous: THE JENSEN INEQUALITY
The most familiar example of a Jensen inequality occurs
when the weights are all equal to 1/N
and the convex function is f(x) = x2.
In this case the Jensen inequality
gives the familiar result
that the mean square exceeds the square of the mean:
| 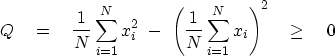 |
(4) |
In the other applications we will consider,
the population consists of positive members,
so the function f(p) need have a positive second derivative
only for positive values of p.
The function f(p)=1/p yields a Jensen inequality for the
harmonic mean:
| 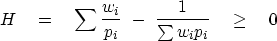 |
(5) |
A more important case is the
geometric inequality.
Here 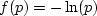 , and
, and
| 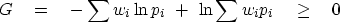 |
(6) |
The more familiar form of the geometric inequality
results from exponentiation and a choice of weights equal to 1/N:
| 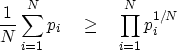 |
(7) |
In other words,
the product of square roots of two values is smaller
than half the sum of the values.
A Jensen inequality with an adjustable parameter
is suggested by 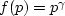 :
:
| 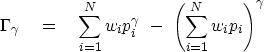 |
(8) |
Whether 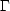 is always positive or always negative
depends upon the numerical value of
is always positive or always negative
depends upon the numerical value of 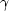 .In practice we may see the dimensionless form,
in which the ratio instead of the difference of the two terms is used.
.In practice we may see the dimensionless form,
in which the ratio instead of the difference of the two terms is used.
A most important inequality in information theory and thermodynamics
is the one based on 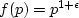 ,where
,where  is a small positive number tending to zero.
I call this the ``weak" inequality.
With some calculation we will quickly arrive at the limit:
is a small positive number tending to zero.
I call this the ``weak" inequality.
With some calculation we will quickly arrive at the limit:
| 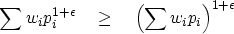 |
(9) |
Take logarithms
|  |
(10) |
Expand both sides in a Taylor series in powers of  using
using
| 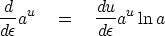 |
(11) |
The leading term is identical on both sides and can be canceled.
Divide both sides by  and go to the limit
and go to the limit 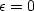 ,obtaining
,obtaining
| 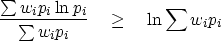 |
(12) |
We can now define a positive variable S'
with or without a positive scaling factor 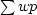 :
:
| 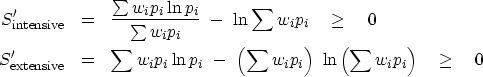 |
(13) |
| (14) |
Seismograms often contain zeros and gaps.
Notice that a single zero pi
can upset the harmonic H or geometric G inequality,
but a single zero has no horrible effect on S or  .
.





Next: RELATED CONCEPTS
Up: THE JENSEN INEQUALITY
Previous: THE JENSEN INEQUALITY
Stanford Exploration Project
10/21/1998
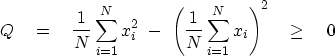
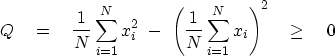
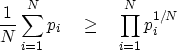
![]() :
:
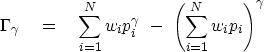
![]() ,where
,where ![]() is a small positive number tending to zero.
I call this the ``weak" inequality.
With some calculation we will quickly arrive at the limit:
is a small positive number tending to zero.
I call this the ``weak" inequality.
With some calculation we will quickly arrive at the limit: