




Next: MIGRATION IN THE (omega,x)-DOMAIN
Up: WAVEMOVIE PROGRAM
Previous: Including lateral velocity variation
Theory predicts that in two dimensions,
waves going through a focus
suffer a 90 phase shift.
You should be able to notice that a symmetrical waveform
is incident on the focus, but an antisymmetrical waveform emerges.
This is easily seen in Figure 10.
trick
phase shift.
You should be able to notice that a symmetrical waveform
is incident on the focus, but an antisymmetrical waveform emerges.
This is easily seen in Figure 10.
trick
Figure 10
The accuracy of the x-derivative may be improved by
a technique that is analyzed later in chapter ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) .
Briefly, instead of
representing
.
Briefly, instead of
representing 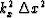 by the tridiagonal
matrix
by the tridiagonal
matrix 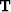 with (-1,2,-1) on the main diagonal,
you use
with (-1,2,-1) on the main diagonal,
you use 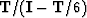 . Modify the extrapolation analysis by multiplying through
by the denominator.
Make the necessary changes to the 45
. Modify the extrapolation analysis by multiplying through
by the denominator.
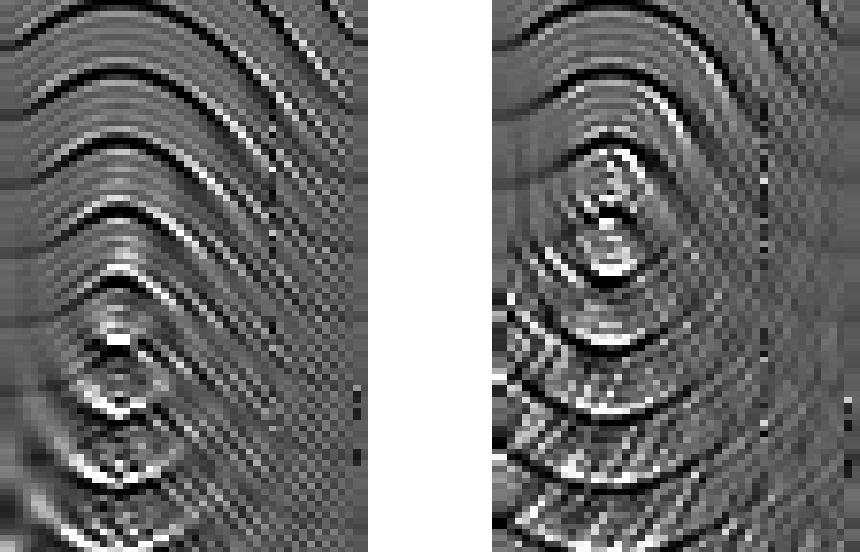
Make the necessary changes to the 45 collapsing wave program.
Left without 1/6 trick; right, with 1/6 trick.
collapsing wave program.
Left without 1/6 trick; right, with 1/6 trick.





In migrations, waves go just to a focus, not through it.
So the migration impulse response in two dimensions
carries a 45 phase shift.
Even though real life is three dimensional,
the two-dimensional response is appropriate
for migrating seismic lines where focusing
is presumed to arise from cylindrical, not spherical, reflectors.
phase shift.
Even though real life is three dimensional,
the two-dimensional response is appropriate
for migrating seismic lines where focusing
is presumed to arise from cylindrical, not spherical, reflectors.
Mabsorbside
Figure 11
Chapter ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) explains how to absorb energy
at the side boundaries.
Make the necessary changes to the program
to absorb waves incident on the left-side boundary. explains how to absorb energy
at the side boundaries.
Make the necessary changes to the program
to absorb waves incident on the left-side boundary.
|
|  |










Next: MIGRATION IN THE (omega,x)-DOMAIN
Up: WAVEMOVIE PROGRAM
Previous: Including lateral velocity variation
Stanford Exploration Project
10/31/1997
![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) .
Briefly, instead of
representing
.
Briefly, instead of
representing 
![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) .
Briefly, instead of
representing
.
Briefly, instead of
representing ![]() phase shift.
Even though real life is three dimensional,
the two-dimensional response is appropriate
for migrating seismic lines where focusing
is presumed to arise from cylindrical, not spherical, reflectors.
phase shift.
Even though real life is three dimensional,
the two-dimensional response is appropriate
for migrating seismic lines where focusing
is presumed to arise from cylindrical, not spherical, reflectors.
![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) explains how to absorb energy
at the side boundaries.
Make the necessary changes to the program
to absorb waves incident on the left-side boundary.
explains how to absorb energy
at the side boundaries.
Make the necessary changes to the program
to absorb waves incident on the left-side boundary.
