




Next: Example of deconvolution with
Up: HOW TO DIVIDE NOISY
Previous: Dividing by zero smoothly
Equation (12) is the solution to an optimization problem
that arises in many applications.
Now that we know the solution, let us formally define the problem.
First, we will solve a simpler problem with real values:
we will choose to minimize the quadratic function of x:
| 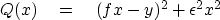 |
(14) |
The second term is called a ``damping factor"
because it prevents x from going to 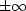 when
when 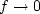 .Set dQ/dx=0, which gives
.Set dQ/dx=0, which gives
| 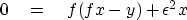 |
(15) |
This yields the earlier answer 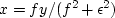 .
.
With Fourier transforms,
the signal X is a complex number at each frequency  .So we generalize equation (14) to
.So we generalize equation (14) to
| 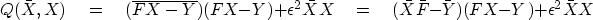 |
(16) |
To minimize Q we could use a real-values approach,
where we express
X=u+iv in terms of two real values u and v
and then set 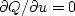 and
and 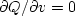 .The approach we will take, however,
is to use complex values,
where we set
.The approach we will take, however,
is to use complex values,
where we set
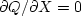 and
and 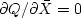 .Let us examine
.Let us examine 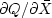 :
:
| 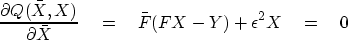 |
(17) |
The derivative 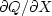 is
the complex conjugate of
is
the complex conjugate of 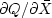 .So if either is zero, the other is too.
Thus we do not need to specify both
.So if either is zero, the other is too.
Thus we do not need to specify both
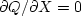 and
and 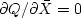 .I usually set
.I usually set
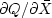 equal to zero.
Solving equation (17) for X
gives equation (12).
equal to zero.
Solving equation (17) for X
gives equation (12).





Next: Example of deconvolution with
Up: HOW TO DIVIDE NOISY
Previous: Dividing by zero smoothly
Stanford Exploration Project
10/21/1998
![]() .So we generalize equation (14) to
.So we generalize equation (14) to