Next: Full separation
Up: SPLITTING AND FULL SEPARATION
Previous: The heat-flow equation
The splitting method
for numerically solving
the heat-flow equation
is to replace the two-dimensional heat-flow equation
by two one-dimensional equations,
each of which is used on alternate time steps:
| 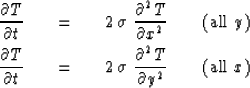 |
(2) |
| (3) |
In equation (2) the heat conductivity  has been
doubled for flow in the x-direction and zeroed for
flow in the y-direction.
The reverse applies in equation (3).
At odd moments in time heat flows according to (2) and
at even moments in time it flows according to (3).
This solution by alternation between (2) and (3)
can be proved mathematically to converge to the solution to
(1) with errors of the order of
has been
doubled for flow in the x-direction and zeroed for
flow in the y-direction.
The reverse applies in equation (3).
At odd moments in time heat flows according to (2) and
at even moments in time it flows according to (3).
This solution by alternation between (2) and (3)
can be proved mathematically to converge to the solution to
(1) with errors of the order of 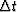 .Hence the error goes to zero as
.Hence the error goes to zero as 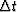 goes to zero.
The motivation for splitting is the infeasibility of higher-dimensional
implicit methods.
goes to zero.
The motivation for splitting is the infeasibility of higher-dimensional
implicit methods.





Next: Full separation
Up: SPLITTING AND FULL SEPARATION
Previous: The heat-flow equation
Stanford Exploration Project
10/31/1997