




Next: The explicit heat-flow equation
Up: FINITE DIFFERENCING
Previous: First derivatives, explicit method
Let us solve the equation
| 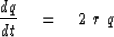 |
(24) |
by numerical methods.
The most obvious (but not the only) approach is the basic definition of
elementary calculus.
For the time derivative, this is
| 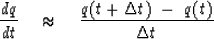 |
(25) |
Using this in equation (24) yields the
the inflation-of-money equations (22) and (23),
where 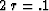 .Thus in the inflation-of-money equation
the expression of dq/dt is centered at
.Thus in the inflation-of-money equation
the expression of dq/dt is centered at 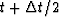 ,whereas the expression of q by itself is at time t.
There is no reason the q on the right side of equation (24)
cannot be averaged at time t
with time
,whereas the expression of q by itself is at time t.
There is no reason the q on the right side of equation (24)
cannot be averaged at time t
with time 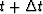 ,thus centering the
whole equation at
,thus centering the
whole equation at 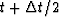 .When writing difference equations,
it is customary to write
.When writing difference equations,
it is customary to write 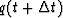 more simply as qt+1.
(Formally one should say
more simply as qt+1.
(Formally one should say 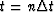 and write qn+1 instead of
qt+1, but helpful mnemonic information is carried by using
t as the subscript instead of some integer like n.)
Thus, a centered approximation of (24) is
and write qn+1 instead of
qt+1, but helpful mnemonic information is carried by using
t as the subscript instead of some integer like n.)
Thus, a centered approximation of (24) is
| 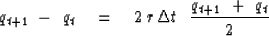 |
(26) |
Letting 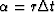 , this becomes
, this becomes
| 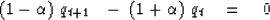 |
(27) |
which is representable as the difference star
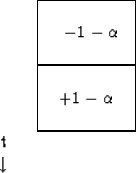
For a fixed 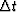 this star gives
a more accurate solution to the differential
equation (24) than does the star for the inflation of money.
The reasons for the names ``explicit method'' and ``implicit method''
above will become clear only after we study a more complicated
equation such as the heat-flow equation.
this star gives
a more accurate solution to the differential
equation (24) than does the star for the inflation of money.
The reasons for the names ``explicit method'' and ``implicit method''
above will become clear only after we study a more complicated
equation such as the heat-flow equation.





Next: The explicit heat-flow equation
Up: FINITE DIFFERENCING
Previous: First derivatives, explicit method
Stanford Exploration Project
10/31/1997

![]() this star gives
a more accurate solution to the differential
equation (24) than does the star for the inflation of money.
The reasons for the names ``explicit method'' and ``implicit method''
above will become clear only after we study a more complicated
equation such as the heat-flow equation.
this star gives
a more accurate solution to the differential
equation (24) than does the star for the inflation of money.
The reasons for the names ``explicit method'' and ``implicit method''
above will become clear only after we study a more complicated
equation such as the heat-flow equation.