We will establish the following theorems about exponentials, logarithms, and powers of Fourier transforms of filters:
To establish theorem 1, define the Z-transform of an arbitrary causal function
| |
(51) |
| |
(52) |
To establish theorem 2, that the exponential is not just causal but also minimum phase, consider
| |
(53) | |
| (54) |
Now we will establish the converse of theorem 2--namely, theorem 3--which states that the logarithm of a minimum-phase filter is causal. Take the logarithm of (52) and form the Z-derivative:
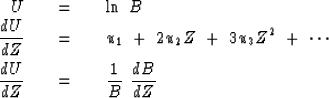 |
(55) | |
| (56) | ||
| (57) |
Theorem 4 refers to the Fourier domain representation
of the minimum-phase filter.
In the complex plane, the filter gives parametric equations
for a curve,
say ![]() .The phase angle
.The phase angle ![]() is defined by the arctangent of the
ratio y/x.
For example, the causal, non-minimum-phase
filter
is defined by the arctangent of the
ratio y/x.
For example, the causal, non-minimum-phase
filter ![]() gives the parametric
equations
gives the parametric
equations ![]() and
and ![]() which define
a circle surrounding the origin.
Notice that the phase
of
which define
a circle surrounding the origin.
Notice that the phase
of ![]() is
is ![]() , which
is a monotonically increasing function of
, which
is a monotonically increasing function of ![]() .In the minimum phase case,
.In the minimum phase case,
![]() .In the non-minimum-phase case,
the curve loops the origin,
so
.In the non-minimum-phase case,
the curve loops the origin,
so ![]() .Theorem 3 allows us to say that
a general formula for minimum-phase filters is
.Theorem 3 allows us to say that
a general formula for minimum-phase filters is
![\begin{eqnarray}
\ \ \ B \eq e^{U(Z)} \ \ \ &=&\ \ \
\exp \left( \
\sum_{{k=0}...
...\right)
\\ \ &=&\ \ \ \exp [r( \omega ) \ +\ i \ \phi ( \omega )]\end{eqnarray}](img170.gif) |
(58) | |
| (59) |
On to theorem 5, which says that any power of a minimum-phase function is minimum phase. Consider
| |
(60) |
Finally the proof of theorem 6, that an impedance function can be
raised to any real fractional power ![]() and the result
will still be an impedance function.
An impedance function is defined to be a minimum-phase function
with the additional property that the real part of its Fourier transform
is positive.
This means that the phase angle
and the result
will still be an impedance function.
An impedance function is defined to be a minimum-phase function
with the additional property that the real part of its Fourier transform
is positive.
This means that the phase angle ![]() lies in the range
lies in the range
![]() .Raising the impedance function to the
.Raising the impedance function to the ![]() power will compress
the range to
power will compress
the range to ![]() .This will keep the real part
of the impedance function positive.
Theorem 5 states that any power
of a minimum-phase function is causal,
which is more than we need to be certain that a
fractional
real power of an impedance function will be causal.
.This will keep the real part
of the impedance function positive.
Theorem 5 states that any power
of a minimum-phase function is causal,
which is more than we need to be certain that a
fractional
real power of an impedance function will be causal.