




Next: Solving for the extrapolation
Up: REFERENCES
Previous: Generalized Riemannian Geometry
The acoustic wave-equation for wavefield, 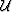 , in a generalized
Riemannian space is
, in a generalized
Riemannian space is
| 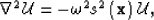 |
(19) |
where the 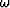 is frequency,
is frequency,  is the propagation slowness, and
is the propagation slowness, and
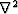 is the Laplacian operator
is the Laplacian operator
| 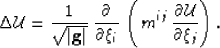 |
(20) |
Substituting equation 20 into 19 generates
a Helmholtz equation appropriate for propagating waves through a 3D
space
| 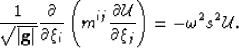 |
(21) |
Expanding the derivative terms and multiplying through by 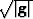 yields
yields
| 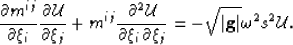 |
(22) |
Defining nj as
| 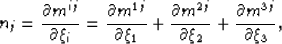 |
(23) |
leads to a more compact notation of equation 22
| 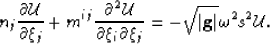 |
(24) |
Developing a wave-equation dispersion relation is achieved by
replacing the partial differential operators acting on wavefield
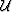 with their Fourier domain duals
with their Fourier domain duals
| 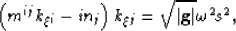 |
(25) |
where 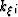 is the Fourier domain dual of differential operator
is the Fourier domain dual of differential operator
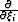 . Equation 25 represents
the dispersion relationship for wavefield propagation on a generalized
3-D Riemannian space.
. Equation 25 represents
the dispersion relationship for wavefield propagation on a generalized
3-D Riemannian space.





Next: Solving for the extrapolation
Up: REFERENCES
Previous: Generalized Riemannian Geometry
Stanford Exploration Project
1/16/2007