Next: Norm of residual
Up: Dip misfit by crossproduct
Previous: Dip misfit by crossproduct
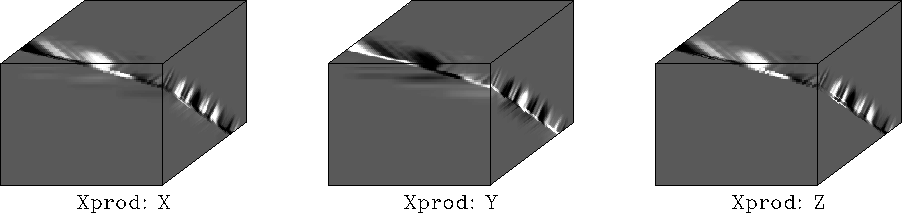
Figure 25
shows the cross-product output for
the synthetic test case of Figure 4.
Each component of the local residual vectors
is displayed as an individual image volume.
In the regions away from the fault,
where the image satisfies the plane-wave assumption,
the residual is zero.
At the fault,
the output image is non-zero
and the fault is broadly outlined.
Within a patch that straddles the fault,
the plane-wave dip estimation
encounters two contradictory plane-wave events.
The least-squares solution averages the two dips
so that the dip estimate does not approximate either of the two dips.
Consequently, within a patch that straddles the fault,
all pixels show a significant residual.
The patch-wide residual
reduces the resolution of the discontinuity image to the
size of the patches and
does not imply a meaningful interpretation
of the discontinuity amplitude.
Because a three-dimensional vector field is difficult to
interpret, the schemes of the two next sections summarize
the information of the three volumes
into a single discontinuity image.
zeroFoltDXG
Figure 25
Cross-product operator applied to synthetic image.
The cross-product operator applied to the synthetic fault model
broadly delineates the fault in each of its three output volumes.
Each output volume is a component of the cross-product vector.
However,
the three-dimensional output vector at each pixel of the three-dimensional
image is not suited to interpretation.










Next: Norm of residual
Up: Dip misfit by crossproduct
Previous: Dip misfit by crossproduct
Stanford Exploration Project
3/8/1999