Next: Data compression
Up: APPLICATIONS
Previous: APPLICATIONS
As in Fourier space, padding zeroes to the detail end of the wavelet vector
interpolates the time series after transforming the vector
back to the time domain.
In contrast to interpolation in the Fourier domain,
the base functions of the wavelet transform are local, and the extended
spectrum contains small but noticeable energy as seen in Figure 6.
In the case of a Haar transform, we would implement a next neighbour
interpolation.
opol
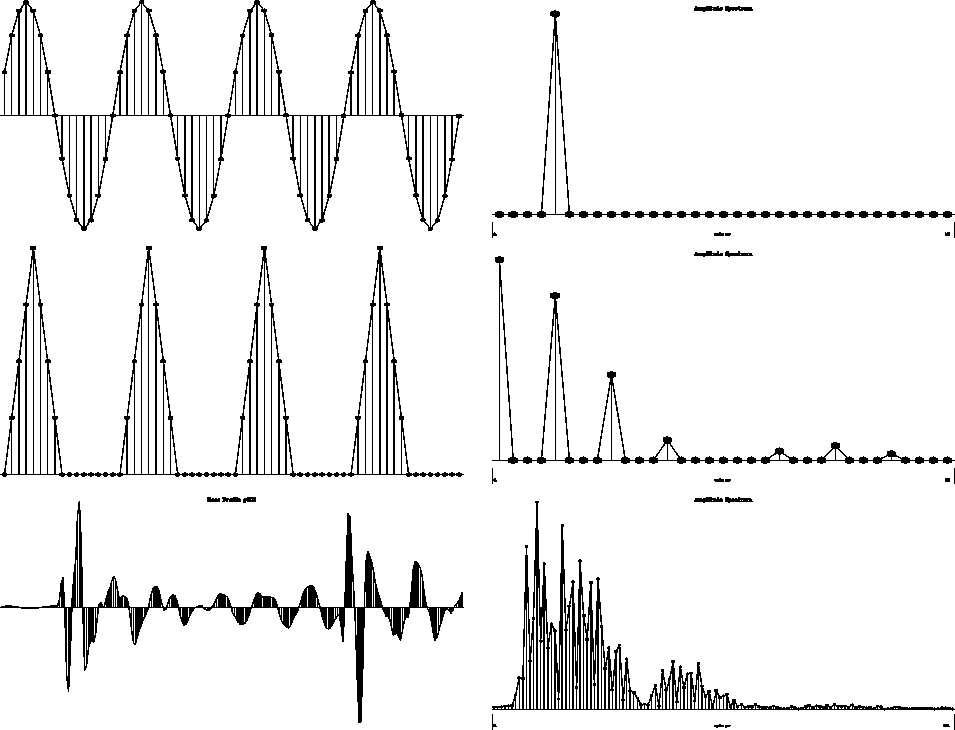
Figure 5
The original test functions and their spectra.
The result of interpolating these functions is displayed in Figure 6.





ipol
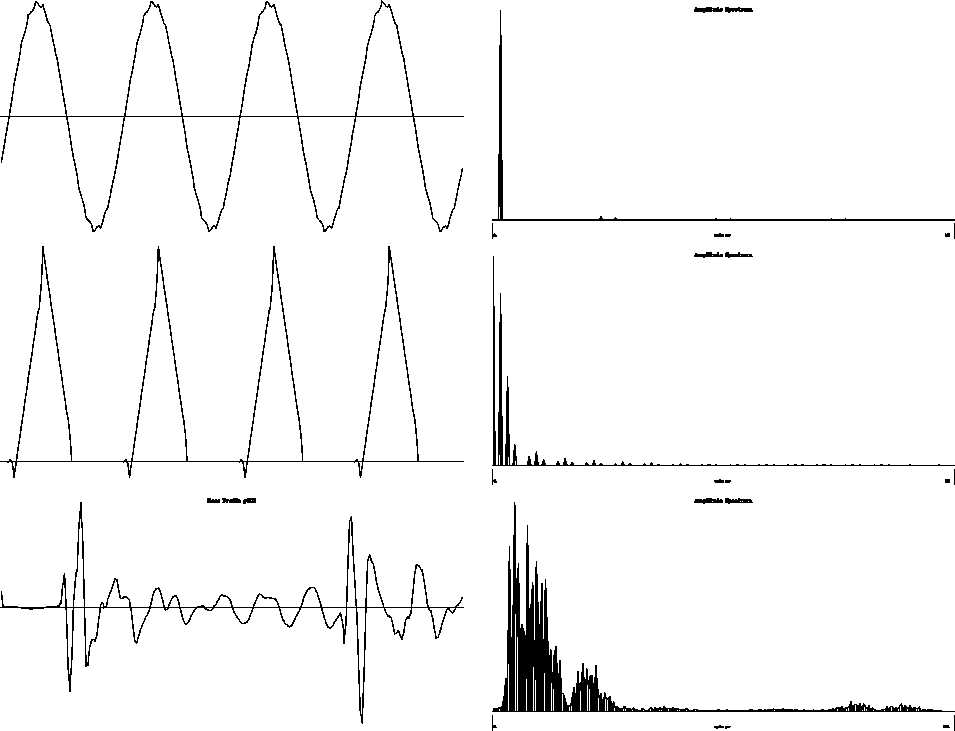
Figure 6
Interpolation by discrete wavelet transformation.
Traces of 256 samples are oversampled by transforming them into the
wavelet domain, padding 256 zeroes at the high-frequency end, and
inverse transforming them. The triangle and sinusoid
series are distorted. The spikiness in time may be realistic
in the trace example. Most, but not all, of the high-frequency
energy is caused by the transforms wraparound feature.
The characteristics of this interpolation scheme remain to be studied.










Next: Data compression
Up: APPLICATIONS
Previous: APPLICATIONS
Stanford Exploration Project
11/18/1997