Next: The NMO velocity
Up: Introduction
Previous: Introduction
The need for Dip Moveout appeared from the problem
of stacking traces that share the same Common-Mid-Point (CMP).
The CMP Stacking assumes that reflections come from horizontal layers.
Under this assumption the Normal Moveout correction (NMO) flattens
the hyperbolas in a CMP gather to horizontal lines.
After NMO, traces belonging to the same CMP are summed
together (stacked) to enhance the reflected signal
and to attenuate the noise.
Problems appear when dipping events are present in a section.
A dipping reflector in a CMP
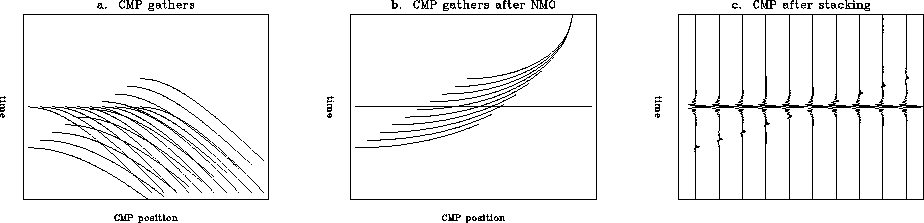
section also appears as a hyperbola (see Figure ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) a).
The NMO velocity necessary to flatten the hyperbolas
originating from reflections on the dipping
layer is higher than the real velocity.
Applying the
NMO correction with the velocity necessary to
flatten this hyperbola will misplace the position
of the dipping reflector.
a).
The NMO velocity necessary to flatten the hyperbolas
originating from reflections on the dipping
layer is higher than the real velocity.
Applying the
NMO correction with the velocity necessary to
flatten this hyperbola will misplace the position
of the dipping reflector.
Figure ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) a shows several CMP gathers
containing reflections from a dipping layer
and from a horizontal layer. After NMO with
the real velocity the hyperbolas corresponding
to the flat layer become straight lines (Figure
a shows several CMP gathers
containing reflections from a dipping layer
and from a horizontal layer. After NMO with
the real velocity the hyperbolas corresponding
to the flat layer become straight lines (Figure ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) b)
and after stacking, the horizontal event is preserved
at the expense of the dipping event. In Figure
b)
and after stacking, the horizontal event is preserved
at the expense of the dipping event. In Figure ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) b
NMO is performed with a higher velocity which is necessary to
flatten the hyperbolas corresponding to the dipping
event. After stacking (Figure
b
NMO is performed with a higher velocity which is necessary to
flatten the hyperbolas corresponding to the dipping
event. After stacking (Figure ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) c) the dipping
event is preserved at the expense of the horizontal
layer. It is obvious that the NMO correction
with a single velocity combined with CMP stacking acts as
a dip filter. The result is a degradation of the
final image when conflicting dips are present.
c) the dipping
event is preserved at the expense of the horizontal
layer. It is obvious that the NMO correction
with a single velocity combined with CMP stacking acts as
a dip filter. The result is a degradation of the
final image when conflicting dips are present.
CMPnmoEx1
Figure 1 The effect of CMP stacking with real velocity on dipping reflectors.
a. Several CMP gathers for a flat layer and a dipping layer.
b. The CMP gathers after NMO with medium velocity (vreal); the
hyperbolas from the horizontal event are flattened.
c. Traces after stacking for the same CMP.
 CMPnmoEx2
CMPnmoEx2
Figure 2 The effect of CMP stacking with velocity 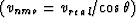 on horizontal reflectors.
on horizontal reflectors.
a. Several CMP gathers for a flat layer and a dipping layer.
b. The CMP gathers after NMO with higher velocity; the hyperbolas
from the dipping event are flattened.
c. Traces after stacking for the same CMP.






Next: The NMO velocity
Up: Introduction
Previous: Introduction
Stanford Exploration Project
11/18/1997
![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) a).
The NMO velocity necessary to flatten the hyperbolas
originating from reflections on the dipping
layer is higher than the real velocity.
Applying the
NMO correction with the velocity necessary to
flatten this hyperbola will misplace the position
of the dipping reflector.
a).
The NMO velocity necessary to flatten the hyperbolas
originating from reflections on the dipping
layer is higher than the real velocity.
Applying the
NMO correction with the velocity necessary to
flatten this hyperbola will misplace the position
of the dipping reflector.