




Next: THE LINEAR SYSTEM
Up: Michelena: SVD
Previous: Introduction
Any MxN-matrix 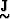 can be decomposed in the following way (Golub and
Van Loan, 1989):
can be decomposed in the following way (Golub and
Van Loan, 1989):
| 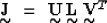 |
(1) |
where 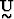 is an MxM orthogonal matrix of eigenvectors that span the
data space,
is an MxM orthogonal matrix of eigenvectors that span the
data space, 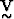 is an NxN orthogonal matrix of eigenvectors that
span the model parameters space and
is an NxN orthogonal matrix of eigenvectors that
span the model parameters space and 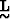 is an MxN diagonal matrix
whose diagonal elements are the singular values of
is an MxN diagonal matrix
whose diagonal elements are the singular values of 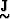 . The columns of
. The columns of
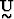 are the eigenvectors of
are the eigenvectors of 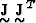 and the columns of
and the columns of 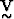 are
the eigenvectors of
are
the eigenvectors of 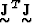 .
.
When a singular
value is zero, the corresponding eigenvector in data (or model) space
cannot be mapped
into model (or data) space. When a singular value is not zero
but is small compared with the largest one (large condition
number), the contribution of the corresponding eigenvectors
into the solution must be eliminated or attenuated (regularization)
because the problem may become unstable.





Next: THE LINEAR SYSTEM
Up: Michelena: SVD
Previous: Introduction
Stanford Exploration Project
12/18/1997
![]() can be decomposed in the following way (Golub and
Van Loan, 1989):
can be decomposed in the following way (Golub and
Van Loan, 1989):