




Next: Fourier-transformation
Up: 2: THE STANDARD DISCONTINUITIES
Previous: The operators and
There is a very important case of discontinuity: 1/t. It does not belong to
our set of standard discontinuities. It will be useful to expand our set of
discontinuities by introducing the Hilbert transformation:
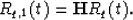
We see that 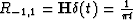 . But what about Rq,1 for
q>-1? Unfortunately, the integral:
. But what about Rq,1 for
q>-1? Unfortunately, the integral:
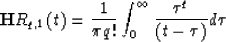
does not exist because of the non-integrable singularity at the point  =0.
But we may use the following trick: if q>-1, we apply the operator
=0.
But we may use the following trick: if q>-1, we apply the operator 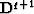 and obtain the discontinuity R-1. After that we may apply the Hilbert
transformation
and obtain the discontinuity R-1. After that we may apply the Hilbert
transformation 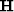 and then the inverse operator
and then the inverse operator 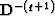 .
.
Remembering the equation (14), we get:
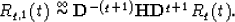
This is a definition of the Hilbert transformation for discontinuities. We
define also:
![\begin{displaymath}
R_{q,\nu}(t)=\left[\cos({\pi\nu\over 2}){\bf E} + \sin({\pi\nu\over 2}){\bf H}
\right]R_q(t) \equiv {\bf H}^{\nu}R_q(t) \end{displaymath}](img104.gif)
where 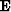 is the unit operator.
is the unit operator.





Next: Fourier-transformation
Up: 2: THE STANDARD DISCONTINUITIES
Previous: The operators and
Stanford Exploration Project
1/13/1998
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()