|
|
|
|
Early-arrival waveform inversion for near-surface velocity and anisotropic parameters: inversion of synthetic data |
Xukai Shen
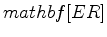 . A model space parametrized by the squares of vertical and horizontal velocity results in vertical velocity and
. A model space parametrized by the squares of vertical and horizontal velocity results in vertical velocity and 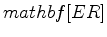 updates with opposite signs. On the other hand, a model space parametrized by the logarithm of the vertical velocity squared and
updates with opposite signs. On the other hand, a model space parametrized by the logarithm of the vertical velocity squared and 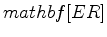 has more reasonable updates, as well as better data matching. However, ambiguity does exist in the inversion results between vertical velocity and
has more reasonable updates, as well as better data matching. However, ambiguity does exist in the inversion results between vertical velocity and 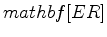 . I clearly demonstrate these findings using a synthetic example.
. I clearly demonstrate these findings using a synthetic example.