|
|
|
|
VTI migration velocity analysis using RTM |
Since first reported in exploration seismology in the 1930s (McCollum and Snell, 1932), anisotropy has become increasingly important in seismic imaging and exploration. The increasing offset and azimuth in data acquisition has heightened the need for anisotropic imaging and model building. Until now, the transverse isotropic (TI) model has been one most commonly used in seismic imaging and has been considered a better description of the subsurface. Li and Biondi (2011) extend the WEMVA framework to VTI media using the one-way wave-equation. However, the one-way wave-equation cannot accurately describe the wave propagation at large angles with respect to vertical, where anisotropy has larger effects. There have been extensive studies on anisotropic RTM with increasingly complex subsurface models (Zhang and Zhang, 2009; Fletcher et al., 2009), but reliable anisotropic model-building techniques are still needed.
Therefore, we propose an image-space WEMVA method using a VTI two-way wave-equation as the propagation engine, and evaluate the flatness of the RTM images in the angle domain. In this paper, we first derive the gradient
of the differential semblance optimization (DSO) objective function with respect to velocity and 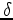 using a Lagrangian augmented functional. To resolve the ambiguity between velocity and
using a Lagrangian augmented functional. To resolve the ambiguity between velocity and 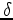 and ensure
that our model honors the geology, we use a preconditioning inversion scheme. Finally, we test the proposed method on a synthetic VTI Marmousi model.
and ensure
that our model honors the geology, we use a preconditioning inversion scheme. Finally, we test the proposed method on a synthetic VTI Marmousi model.
|
|
|
|
VTI migration velocity analysis using RTM |