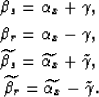
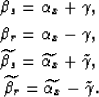 |
(11) | |
| (12) | ||
| (13) | ||
| (14) |
From a ``plane-wave'' viewpoint, the image point in the angle-domain
is determined by the intersection of the lines passing through the
points ![]() and tilted by
and tilted by
![]() and
and ![]() . This interpretation
is consistent with the one for flat reflectors illustrated in Figure 3.
. This interpretation
is consistent with the one for flat reflectors illustrated in Figure 3.
|
cig-2d-aniso-dipping-1
Figure 2 Geometry of the transformation to the angle-domain with a dipping reflector. The image point in the subsurface-offset domain | 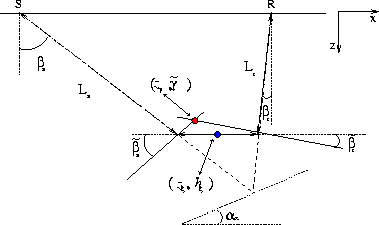 |
|
cig-2d-aniso-flat-v1
Figure 3 Geometry of the transformation to the angle-domain with a flat reflector. The image point in the subsurface-offset domain | 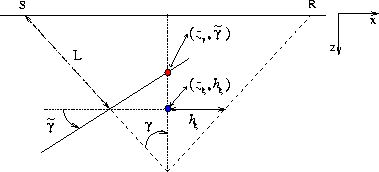 |
The geometric interpretation of the angle ![]() is
illustrated in Figure 4. According to
equation (10), the depth of the
image point in the angle-domain
is
illustrated in Figure 4. According to
equation (10), the depth of the
image point in the angle-domain ![]() is given by the intersection
of the two lines passing through the points
is given by the intersection
of the two lines passing through the points ![]() and tilted by
and tilted by ![]() . For flat
reflectors,
. For flat
reflectors, ![]() Biondi (2005a), which is consistent with
Figure 3.
Biondi (2005a), which is consistent with
Figure 3.
|
cig-2d-aniso-dipping-2
Figure 4 Geometric interpretation of the angle | 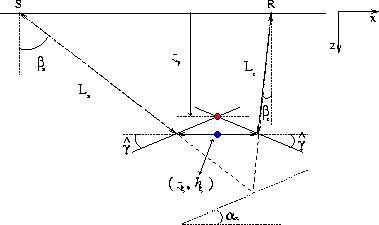 |