




Next: Velocity analysis
Up: Artman: Inversion shortcuts
Previous: Synthetic example
To understand the sources captured in a passive seismic survey, I
hoped planewave decomposition/inversion could help analyze the
data. However, unless identifiable events are present, analysis of
passive data before cross-correlation does not produce interpretable
results. After correlation, the unique character of the individual
sources is lost. In effect, transforms applied to the data before
correlation simply reshuffle the randomness apparent in the raw
traces. The passively collected solar data Rickett and Claerbout (1999) was analyzed to
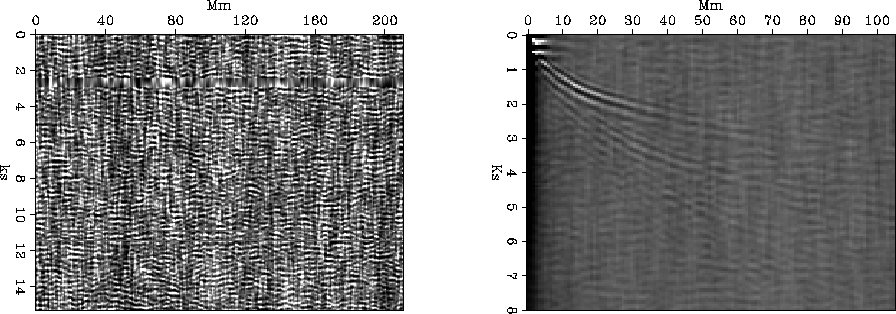
prove this failure. Figure ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) shows the
raw solar data and its autocorrelation. Clearly, there are events to
be found within the raw data that are masked before correlation.
Figure
shows the
raw solar data and its autocorrelation. Clearly, there are events to
be found within the raw data that are masked before correlation.
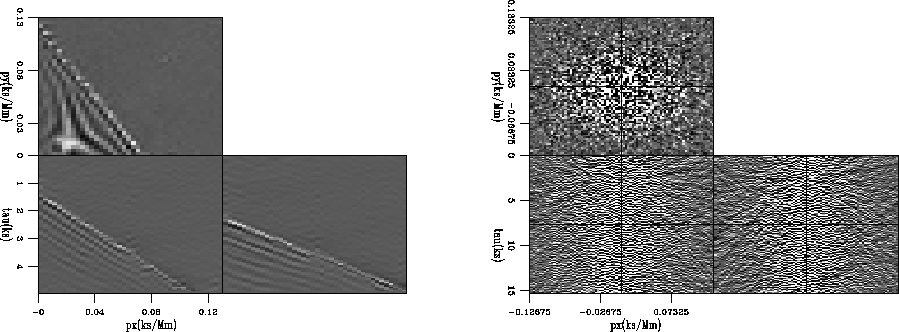
Figure ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) shows the linear Radon domain inversions for
data defined by the panels of Figure
shows the linear Radon domain inversions for
data defined by the panels of Figure ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) .
Because the correlated data is radially symmetric from the center and
only has events in the upper third of the time axis, its
model space is much smaller, though sampling between the two is the
same.
sun.dat
.
Because the correlated data is radially symmetric from the center and
only has events in the upper third of the time axis, its
model space is much smaller, though sampling between the two is the
same.
sun.dat
Figure 5 Passive seismic data from the
sun and its autocorrelation.




 sun.mod
sun.mod
Figure 6 Model space produced with 20
iterations of planewave decomposition inversion from the data shown
in Figure ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) .
.










Next: Velocity analysis
Up: Artman: Inversion shortcuts
Previous: Synthetic example
Stanford Exploration Project
4/5/2006
![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) shows the
raw solar data and its autocorrelation. Clearly, there are events to
be found within the raw data that are masked before correlation.
Figure
shows the
raw solar data and its autocorrelation. Clearly, there are events to
be found within the raw data that are masked before correlation.
Figure ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) shows the linear Radon domain inversions for
data defined by the panels of Figure
shows the linear Radon domain inversions for
data defined by the panels of Figure ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) .
Because the correlated data is radially symmetric from the center and
only has events in the upper third of the time axis, its
model space is much smaller, though sampling between the two is the
same.
.
Because the correlated data is radially symmetric from the center and
only has events in the upper third of the time axis, its
model space is much smaller, though sampling between the two is the
same.

![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) .
.