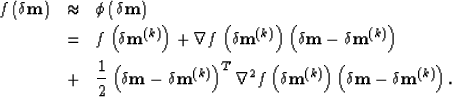
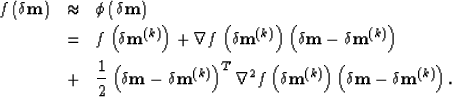 |
||
| (30) |
| |
(31) |
(a) Assign the initial model ![]() and the acceptable error
and the acceptable error ![]() and set the iterative number k=1.
and set the iterative number k=1.
(b) Calculate ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
(c) If ![]() , then stop iteration; otherwise,
, then stop iteration; otherwise, ![]() .
.
(d) Starting from ![]() , carry out 1D searching along the searching direction
, carry out 1D searching along the searching direction ![]() for
for ![]() satisfying
satisfying ![]() .
.
(e) Letting ![]() and k:=k+1, go to step (b).
If the Hessian
and k:=k+1, go to step (b).
If the Hessian ![]() is not positive definite, the Newton algorithm should be modified further. That means
is not positive definite, the Newton algorithm should be modified further. That means ![]() is replaced with
is replaced with ![]() . If the
. If the ![]() is chosen suitably, the matrix
is chosen suitably, the matrix ![]() will be positive definite.
[B] Quasi-Newton algorithm:
The main feature of this algorithm is that the inverse of the Hessian matrix is not explicitly calculated. Further implementing the differential operation on both sides of equation (30) yields
will be positive definite.
[B] Quasi-Newton algorithm:
The main feature of this algorithm is that the inverse of the Hessian matrix is not explicitly calculated. Further implementing the differential operation on both sides of equation (30) yields
| |
(32) |
| |
(33) |
(a) Assign the initial model ![]() and the acceptable error
and the acceptable error ![]() .
.
(b) Setting H1=In and the iterative number k=1, calculate ![]() .
.
(c) Let ![]() .
.
(d) Starting from ![]() , carry out 1D searching along the searching direction
, carry out 1D searching along the searching direction ![]() for
for ![]() satisfying
satisfying ![]() .
.
(e) If ![]() , then stop iteration; otherwise, go to Step (f).
, then stop iteration; otherwise, go to Step (f).
(f) If k=n, then let ![]() , go to Step(b); Otherwise, go to Step (g).
, go to Step(b); Otherwise, go to Step (g).
(g) Letting ![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]() , calculate Hk+1 with any of Formula 1-4. Setting k:=k+1, go to Step (c).
, calculate Hk+1 with any of Formula 1-4. Setting k:=k+1, go to Step (c).