




Next: About this document ...
Up: Shragge and Sava: Migration
Previous: Acknowledgments
- Berryhill, J., 1979, Wave-equation datuming: Geophysics, 44, 1329-1344.
-
- Bevc, D., 1997, Floodint the topography: Wave-equation datuming of land data with rugged acquisition topography: Geophysics, 62, 1558-1569.
-
- Gazdag, J., and Sguazzero, P., 1984, Migration of seismic data by phase-shift plus interpolation: Geophysics, 69, 124-131.
-
- Gray, S., and Marfurt, K., 1995, Migration from topography: Improving the near-surface image: J. Can. Soc. Expl. Geophys., 31, 18-24.
-
- Jiao, J., Trickett, S., and Link, B., 2004, Wave-equation migration of land data: 2004 CSEG Convention, CSEG, CSEG Abstracts.
-
- Kythe, P., 1998, Computational conformal mapping: Birkhäuser, Boston, MA.
-
- Nehari, Z., 1975, Conformal mapping: Dover Publications Inc., New York.
-
- Riemann, B., 1851, Grundlagen für eine allgemeine Theorie der Funktionen einer veränderlichen komplexen grösse (1851) in collected works: Dover Publications Inc, New York.
-
- Sava, P., and Fomel, S., 2004, Seismic imaging using Riemannian wavefield extrapolation: submitted to Geophysics.
-
- Sava, P., 2004, High-order kernels for Riemannian wavefield extrapolation: SEP-117.
-
A
This appendix discusses the conformal mapping between polygons of
arbitrary shape and the upper half plane. Assisting us in this
transformation is an important conformal map transformation, termed
Schwarz-Christoffel mapping, that facilitates solution of a
class of BVPs with polygonal boundaries. Figure ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) illustrates the transformation and also illustrates the basic
nomenclature.
illustrates the transformation and also illustrates the basic
nomenclature.
sctran
Figure 9 Schematic of the Schwarz-Christoffel
transformation between a polygonal domain in the w-plane and the
upper half plane (UHP), 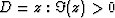 , in the z-plane.
This transformation maps line segments
, in the z-plane.
This transformation maps line segments 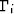 that lie on the
y=0 line in the z-plane to the line segments
that lie on the
y=0 line in the z-plane to the line segments 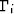 that
define the polygonal boundary of the w-plane according to mapping
rule f. Exterior angles,
that
define the polygonal boundary of the w-plane according to mapping
rule f. Exterior angles, 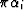 , are used in the
transformation formula, and are defined by
, are used in the
transformation formula, and are defined by 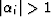 and
and 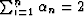 . Points xi in the z-plane
are mapped to points wi in the w-plane.
. Points xi in the z-plane
are mapped to points wi in the w-plane.

The formula for calculating the transformation is,
| 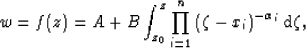 |
(13) |
where A and B are constants that determine the size and position
of the polygon 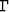 , and
, and 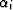 denotes the exterior angle
(see Figure
denotes the exterior angle
(see Figure ![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) ). Constants A and B are computed
after defining the mapping of 3 points (i.e., known points z0).
The integration is carried out along any path in the domain D that
connects known point z0 and the point in question z.
). Constants A and B are computed
after defining the mapping of 3 points (i.e., known points z0).
The integration is carried out along any path in the domain D that
connects known point z0 and the point in question z.
The inverse Schwarz-Christoffel transformation is given by,
| 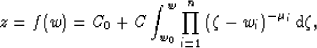 |
(14) |
where 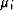 are the interior angles, and integration is carried out
along any path that connects known mapping point w0 with the point
in question w.
are the interior angles, and integration is carried out
along any path that connects known mapping point w0 with the point
in question w.
In numerical applications of Schwarz-Christoffel mapping, it is
necessary to determine numerically the (2n+2) parameters (i.e. all
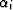 , xi and A, B) that appear in equations (13)
and (14). In conformal mapping literature, this problem
is termed the 'parameter problem' Kythe (1998). The numerical
solution to this problem requires selecting 3 points of the x-axis
that map to 3 preassigned points in the u-axis (i.e. p1, p2 and
p3). This allows for equation (13) to be segmented
into the Schwarz-Christoffel integrals,
, xi and A, B) that appear in equations (13)
and (14). In conformal mapping literature, this problem
is termed the 'parameter problem' Kythe (1998). The numerical
solution to this problem requires selecting 3 points of the x-axis
that map to 3 preassigned points in the u-axis (i.e. p1, p2 and
p3). This allows for equation (13) to be segmented
into the Schwarz-Christoffel integrals,
| 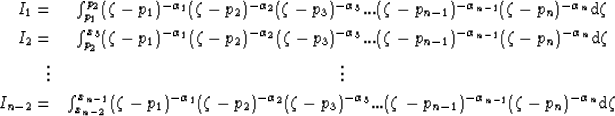 |
|
| (15) |
| |
| |
Fortunately, the ratio of any two sides of the mapped polygon is
independent of scale factors A and B. This allows the parameter
problem to be written as the following series of equations:
| 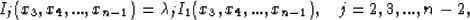 |
(16) |
where
| 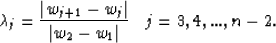 |
(17) |
A solution to the Schwarz-Christoffel integrals begins by expanding the
series of equations (17) in a first order Taylor power
series about initial guesses, xi(0), of the true values,
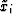 . This leads to a system of equations that may be solved
using Newton's method:
. This leads to a system of equations that may be solved
using Newton's method:
| ![\begin{displaymath}
I_j^{(0)}+\sum_{\nu=3}^{n-1} h_{\nu}^{(1)} \frac{\partial
I...
...rtial I_1^{(0)}}{\partial
x_{\nu}} \right], \;\;\;j=2,...,n-2,\end{displaymath}](img63.gif) |
(18) |
where 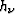 , the correction factors that are being solved for, are
applied to yield the next estimate of the vertex corners,
, the correction factors that are being solved for, are
applied to yield the next estimate of the vertex corners,
| 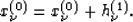 |
(19) |
This process is repeated using nth iterative updates of 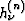 until the desired tolerance is reached. Finally, the
Schwarz-Christoffel integrals are improper because the integrand of
each integral becomes unbounded at the two points of integration.
Kythe (1998) discusses using the Kantorovich method to regularize
these integrals.
until the desired tolerance is reached. Finally, the
Schwarz-Christoffel integrals are improper because the integrand of
each integral becomes unbounded at the two points of integration.
Kythe (1998) discusses using the Kantorovich method to regularize
these integrals.





Next: About this document ...
Up: Shragge and Sava: Migration
Previous: Acknowledgments
Stanford Exploration Project
10/23/2004
![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) illustrates the transformation and also illustrates the basic
nomenclature.
illustrates the transformation and also illustrates the basic
nomenclature.
![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) illustrates the transformation and also illustrates the basic
nomenclature.
illustrates the transformation and also illustrates the basic
nomenclature.

![[*]](http://sepwww.stanford.edu/latex2html/cross_ref_motif.gif) ). Constants A and B are computed
after defining the mapping of 3 points (i.e., known points z0).
The integration is carried out along any path in the domain D that
connects known point z0 and the point in question z.
). Constants A and B are computed
after defining the mapping of 3 points (i.e., known points z0).
The integration is carried out along any path in the domain D that
connects known point z0 and the point in question z.
![]() , xi and A, B) that appear in equations (13)
and (14). In conformal mapping literature, this problem
is termed the 'parameter problem' Kythe (1998). The numerical
solution to this problem requires selecting 3 points of the x-axis
that map to 3 preassigned points in the u-axis (i.e. p1, p2 and
p3). This allows for equation (13) to be segmented
into the Schwarz-Christoffel integrals,
, xi and A, B) that appear in equations (13)
and (14). In conformal mapping literature, this problem
is termed the 'parameter problem' Kythe (1998). The numerical
solution to this problem requires selecting 3 points of the x-axis
that map to 3 preassigned points in the u-axis (i.e. p1, p2 and
p3). This allows for equation (13) to be segmented
into the Schwarz-Christoffel integrals,
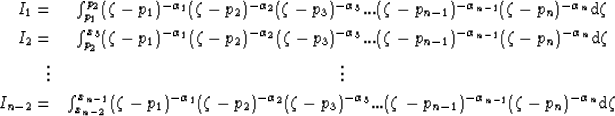
![]() . This leads to a system of equations that may be solved
using Newton's method:
. This leads to a system of equations that may be solved
using Newton's method:
![\begin{displaymath}
I_j^{(0)}+\sum_{\nu=3}^{n-1} h_{\nu}^{(1)} \frac{\partial
I...
...rtial I_1^{(0)}}{\partial
x_{\nu}} \right], \;\;\;j=2,...,n-2,\end{displaymath}](img63.gif)